Inference on one GPU
Efficient Inference on a Single GPU
In addition to this guide, relevant information can be found as well in the guide for training on a single GPU and the guide for inference on CPUs.
Flash Attention 2
Note that this feature is experimental and might considerably change in future versions. For instance, the Flash Attention 2 API might migrate to BetterTransformer API in the near future.
Flash Attention 2 can considerably speed up transformer-based models’ training and inference speed. Flash Attention 2 has been introduced in the official Flash Attention repository by Tri Dao et al. The scientific paper on Flash Attention can be found here.
Make sure to follow the installation guide on the repository mentioned above to properly install Flash Attention 2. Once that package is installed, you can benefit from this feature.
We natively support Flash Attention 2 for the following models:
Llama
Mistral
Falcon
You can request to add Flash Attention 2 support for more models by opening an issue on GitHub, and even open a Pull Request to integrate the changes. The supported models can be used for inference and training, including training with padding tokens - which is currently not supported for BetterTransformer API below.
Flash Attention 2 can only be used when the models’ dtype is fp16 or bf16 and runs only on NVIDIA-GPU devices. Make sure to cast your model to the appropriate dtype and load them on a supported device before using that feature.
Quick usage
To enable Flash Attention 2 in your model, add use_flash_attention_2 in the from_pretrained arguments:
Copied
And use it for generation or fine-tuning.
Expected speedups
You can benefit from considerable speedups for fine-tuning and inference, especially for long sequences. However, since Flash Attention does not support computing attention scores with padding tokens under the hood, we must manually pad / unpad the attention scores for batched inference when the sequence contains padding tokens. This leads to a significant slowdown for batched generations with padding tokens.
To overcome this, one should use Flash Attention without padding tokens in the sequence for training (e.g., by packing a dataset, i.e., concatenating sequences until reaching the maximum sequence length. An example is provided here.
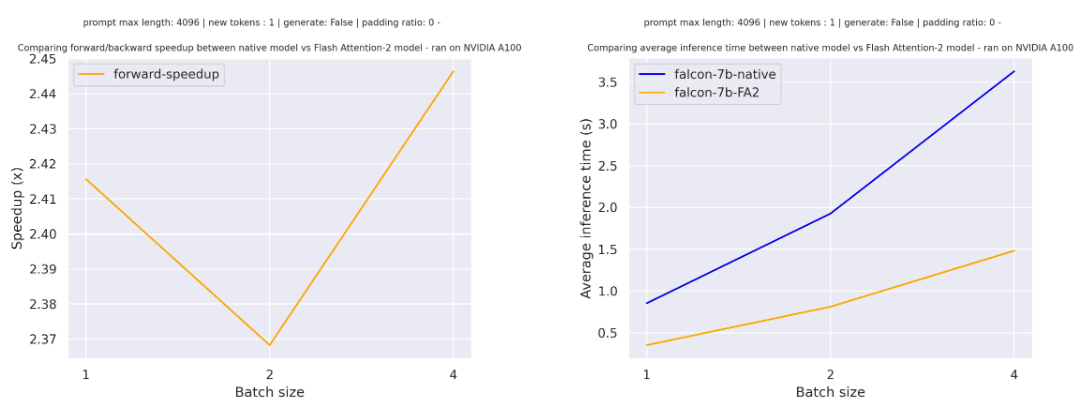
Below is the expected speedup you can get for a simple forward pass on tiiuae/falcon-7b with a sequence length of 4096 and various batch sizes, without padding tokens:
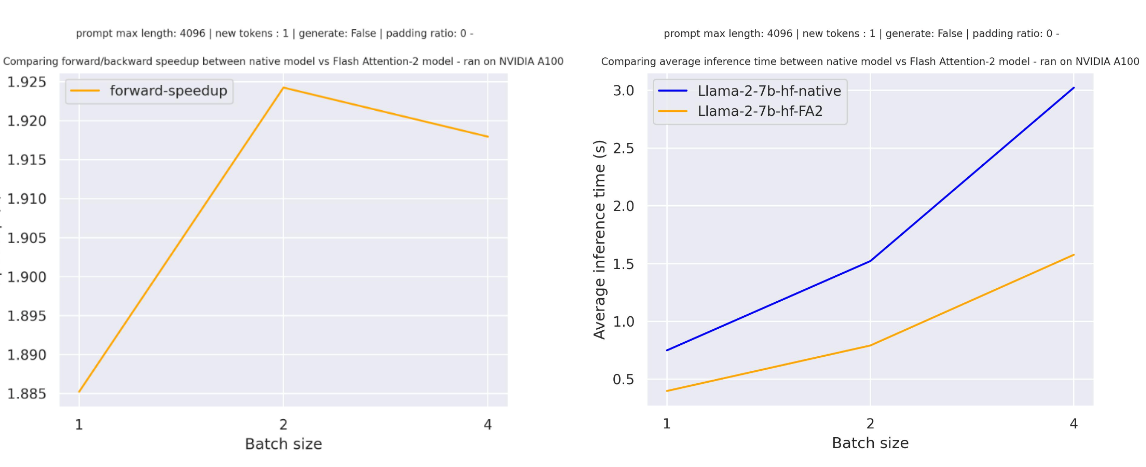
Below is the expected speedup you can get for a simple forward pass on meta-llama/Llama-7b-hf with a sequence length of 4096 and various batch sizes, without padding tokens:
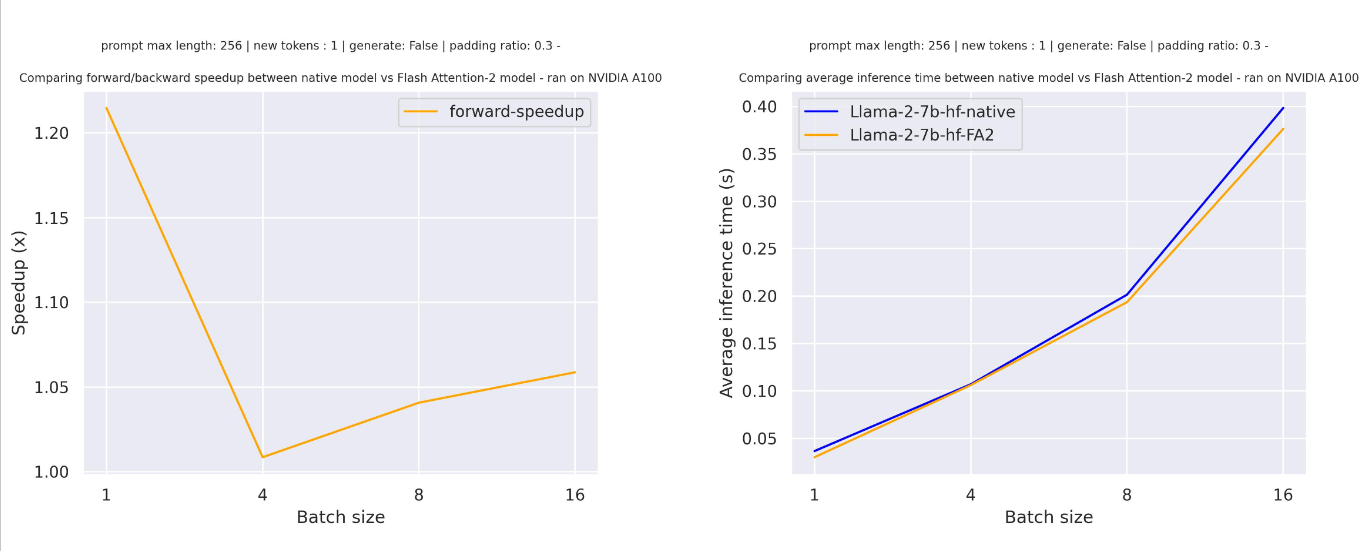
For sequences with padding tokens (training with padding tokens or generating with padding tokens), we need to unpad / pad the input sequences to compute correctly the attention scores. For relatively small sequence length, on pure forward pass, this creates an overhead leading to a small speedup (below 30% of the input has been filled with padding tokens).
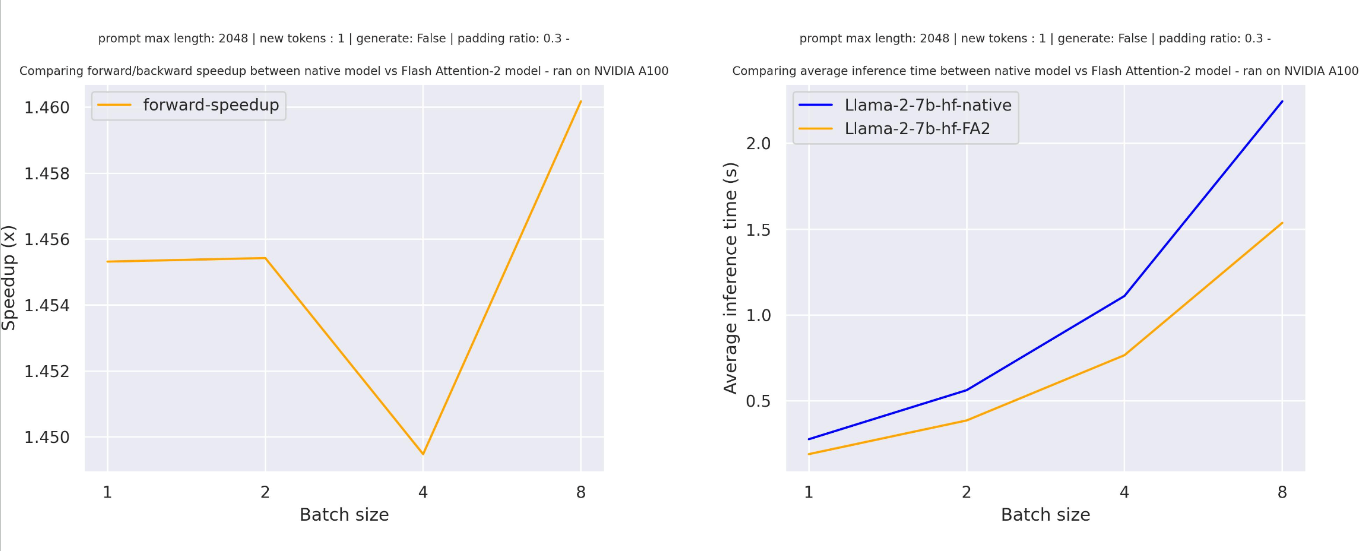
But for large sequence length you can benefit from interesting speedup for pure inference (also training)
Note that Flash Attention makes the attention computation more memory efficient, meaning you can train with much larger sequence lengths without facing CUDA OOM issues. It can lead up to memory reduction up to 20 for large sequence length. Check out the official flash attention repository for more details.
Advanced usage
You can combine this feature with many exisiting feature for model optimization. Check out few examples below:
Combining Flash Attention 2 and 8-bit models
You can combine this feature together with 8-bit quantization:
Copied
Combining Flash Attention 2 and 4-bit models
You can combine this feature together with 4-bit quantization:
Copied
Combining Flash Attention 2 and PEFT
You can combine this feature together with PEFT for training adapters using Flash Attention 2 under the hood:
Copied
BetterTransformer
BetterTransformer converts 🌍 Transformers models to use the PyTorch-native fastpath execution, which calls optimized kernels like Flash Attention under the hood.
BetterTransformer is also supported for faster inference on single and multi-GPU for text, image, and audio models.
Flash Attention can only be used for models using fp16 or bf16 dtype. Make sure to cast your model to the appropriate dtype before using BetterTransformer.
Encoder models
PyTorch-native nn.MultiHeadAttention attention fastpath, called BetterTransformer, can be used with Transformers through the integration in the 🌍 Optimum library.
PyTorch’s attention fastpath allows to speed up inference through kernel fusions and the use of nested tensors. Detailed benchmarks can be found in this blog post.
After installing the optimum package, to use Better Transformer during inference, the relevant internal modules are replaced by calling to_bettertransformer():
Copied
The method reverse_bettertransformer() allows to go back to the original modeling, which should be used before saving the model in order to use the canonical transformers modeling:
Copied
Have a look at this blog post to learn more about what is possible to do with BetterTransformer API for encoder models.
Decoder models
For text models, especially decoder-based models (GPT, T5, Llama, etc.), the BetterTransformer API converts all attention operations to use the torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention operator (SDPA) that is only available in PyTorch 2.0 and onwards.
To convert a model to BetterTransformer:
Copied
SDPA can also call Flash Attention kernels under the hood. To enable Flash Attention or to check that it is available in a given setting (hardware, problem size), use torch.backends.cuda.sdp_kernel as a context manager:
Copied
If you see a bug with a traceback saying
Copied
try using the PyTorch nightly version, which may have a broader coverage for Flash Attention:
Copied
Or make sure your model is correctly casted in float16 or bfloat16
Have a look at this detailed blogpost to read more about what is possible to do with BetterTransformer + SDPA API.
bitsandbytes integration for FP4 mixed-precision inference
You can install bitsandbytes and benefit from easy model compression on GPUs. Using FP4 quantization you can expect to reduce up to 8x the model size compared to its native full precision version. Check out below how to get started.
Note that this feature can also be used in a multi GPU setup.
Requirements
Latest
bitsandbyteslibrarypip install bitsandbytes>=0.39.0Install latest
acceleratefrom sourcepip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.gitInstall latest
transformersfrom sourcepip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
Running FP4 models - single GPU setup - Quickstart
You can quickly run a FP4 model on a single GPU by running the following code:
Copied
Note that device_map is optional but setting device_map = 'auto' is prefered for inference as it will dispatch efficiently the model on the available ressources.
Running FP4 models - multi GPU setup
The way to load your mixed 4-bit model in multiple GPUs is as follows (same command as single GPU setup):
Copied
But you can control the GPU RAM you want to allocate on each GPU using accelerate. Use the max_memory argument as follows:
Copied
In this example, the first GPU will use 600MB of memory and the second 1GB.
Advanced usage
For more advanced usage of this method, please have a look at the quantization documentation page.
bitsandbytes integration for Int8 mixed-precision matrix decomposition
Note that this feature can also be used in a multi GPU setup.
From the paper LLM.int8() : 8-bit Matrix Multiplication for Transformers at Scale, we support Hugging Face integration for all models in the Hub with a few lines of code. The method reduces nn.Linear size by 2 for float16 and bfloat16 weights and by 4 for float32 weights, with close to no impact to the quality by operating on the outliers in half-precision.

Int8 mixed-precision matrix decomposition works by separating a matrix multiplication into two streams: (1) a systematic feature outlier stream matrix multiplied in fp16 (0.01%), (2) a regular stream of int8 matrix multiplication (99.9%). With this method, int8 inference with no predictive degradation is possible for very large models. For more details regarding the method, check out the paper or our blogpost about the integration.

Note, that you would require a GPU to run mixed-8bit models as the kernels have been compiled for GPUs only. Make sure that you have enough GPU memory to store the quarter (or half if your model weights are in half precision) of the model before using this feature. Below are some notes to help you use this module, or follow the demos on Google colab.
Requirements
If you have
bitsandbytes<0.37.0, make sure you run on NVIDIA GPUs that support 8-bit tensor cores (Turing, Ampere or newer architectures - e.g. T4, RTX20s RTX30s, A40-A100). Forbitsandbytes>=0.37.0, all GPUs should be supported.Install the correct version of
bitsandbytesby running:pip install bitsandbytes>=0.31.5Install
acceleratepip install accelerate>=0.12.0
Running mixed-Int8 models - single GPU setup
After installing the required libraries, the way to load your mixed 8-bit model is as follows:
Copied
For text generation, we recommend:
using the model’s
generate()method instead of thepipeline()function. Although inference is possible with thepipeline()function, it is not optimized for mixed-8bit models, and will be slower than using thegenerate()method. Moreover, some sampling strategies are like nucleaus sampling are not supported by thepipeline()function for mixed-8bit models.placing all inputs on the same device as the model.
Here is a simple example:
Copied
Running mixed-int8 models - multi GPU setup
The way to load your mixed 8-bit model in multiple GPUs is as follows (same command as single GPU setup):
Copied
But you can control the GPU RAM you want to allocate on each GPU using accelerate. Use the max_memory argument as follows:
Copied
In this example, the first GPU will use 1GB of memory and the second 2GB.
Colab demos
With this method you can infer on models that were not possible to infer on a Google Colab before. Check out the demo for running T5-11b (42GB in fp32)! Using 8-bit quantization on Google Colab:
Or this demo for BLOOM-3B:
Advanced usage: mixing FP4 (or Int8) and BetterTransformer
You can combine the different methods described above to get the best performance for your model. For example, you can use BetterTransformer with FP4 mixed-precision inference + flash attention:
Copied
Last updated