ViTMatte
ViTMatte
Overview
The ViTMatte model was proposed in Boosting Image Matting with Pretrained Plain Vision Transformers by Jingfeng Yao, Xinggang Wang, Shusheng Yang, Baoyuan Wang. ViTMatte leverages plain Vision Transformers for the task of image matting, which is the process of accurately estimating the foreground object in images and videos.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
Recently, plain vision Transformers (ViTs) have shown impressive performance on various computer vision tasks, thanks to their strong modeling capacity and large-scale pretraining. However, they have not yet conquered the problem of image matting. We hypothesize that image matting could also be boosted by ViTs and present a new efficient and robust ViT-based matting system, named ViTMatte. Our method utilizes (i) a hybrid attention mechanism combined with a convolution neck to help ViTs achieve an excellent performance-computation trade-off in matting tasks. (ii) Additionally, we introduce the detail capture module, which just consists of simple lightweight convolutions to complement the detailed information required by matting. To the best of our knowledge, ViTMatte is the first work to unleash the potential of ViT on image matting with concise adaptation. It inherits many superior properties from ViT to matting, including various pretraining strategies, concise architecture design, and flexible inference strategies. We evaluate ViTMatte on Composition-1k and Distinctions-646, the most commonly used benchmark for image matting, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance and outperforms prior matting works by a large margin.
Tips:
The model expects both the image and trimap (concatenated) as input. One can use
ViTMatteImageProcessorfor this purpose.
This model was contributed by nielsr. The original code can be found here.
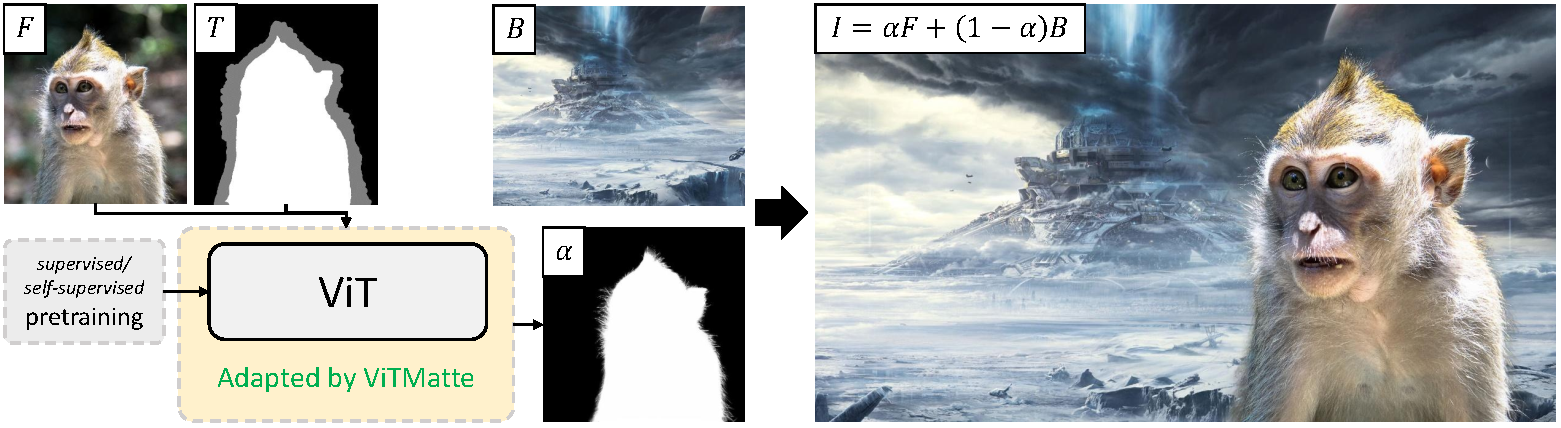
ViTMatte high-level overview. Taken from the original paper.
Resources
A list of official BOINC AI and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with ViTMatte.
A demo notebook regarding inference with VitMatteForImageMatting, including background replacement, can be found here.
VitMatteConfig
class transformers.VitMatteConfig
( backbone_config: PretrainedConfig = Nonehidden_size: int = 384batch_norm_eps: float = 1e-05initializer_range: float = 0.02convstream_hidden_sizes: typing.List[int] = [48, 96, 192]fusion_hidden_sizes: typing.List[int] = [256, 128, 64, 32]**kwargs )
Parameters
backbone_config (
PretrainedConfigordict, optional, defaults toVitDetConfig()) — The configuration of the backbone model.hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 384) — The number of input channels of the decoder.batch_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-5) — The epsilon used by the batch norm layers.initializer_range (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices.convstream_hidden_sizes (
List[int], optional, defaults to[48, 96, 192]) — The output channels of the ConvStream module.fusion_hidden_sizes (
List[int], optional, defaults to[256, 128, 64, 32]) — The output channels of the Fusion blocks.
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of VitMatteForImageMatting. It is used to instantiate a ViTMatte model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the ViTMatte hustvl/vitmatte-small-composition-1k architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
Copied
to_dict
( )
Serializes this instance to a Python dictionary. Override the default to_dict(). Returns: Dict[str, any]: Dictionary of all the attributes that make up this configuration instance,
VitMatteImageProcessor
class transformers.VitMatteImageProcessor
( do_rescale: bool = Truerescale_factor: typing.Union[int, float] = 0.00392156862745098do_normalize: bool = Trueimage_mean: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = Noneimage_std: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = Nonedo_pad: bool = Truesize_divisibility: int = 32**kwargs )
Parameters
do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to rescale the image by the specified scalerescale_factor. Can be overridden by thedo_rescaleparameter in thepreprocessmethod.rescale_factor (
intorfloat, optional, defaults to 1/255) — Scale factor to use if rescaling the image. Can be overridden by therescale_factorparameter in thepreprocessmethod.do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to normalize the image. Can be overridden by thedo_normalizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod.image_mean (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_STANDARD_MEAN) — Mean to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats the length of the number of channels in the image. Can be overridden by theimage_meanparameter in thepreprocessmethod.image_std (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_STANDARD_STD) — Standard deviation to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats the length of the number of channels in the image. Can be overridden by theimage_stdparameter in thepreprocessmethod.do_pad (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to pad the image to make the width and height divisible bysize_divisibility. Can be overridden by thedo_padparameter in thepreprocessmethod.size_divisibility (
int, optional, defaults to 32) — The width and height of the image will be padded to be divisible by this number.
Constructs a ViTMatte image processor.
preprocess
( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), typing.List[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image')], typing.List[numpy.ndarray], typing.List[ForwardRef('torch.Tensor')]]trimaps: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), typing.List[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image')], typing.List[numpy.ndarray], typing.List[ForwardRef('torch.Tensor')]]do_rescale: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonerescale_factor: typing.Optional[float] = Nonedo_normalize: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneimage_mean: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = Noneimage_std: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = Nonedo_pad: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonesize_divisibility: typing.Optional[int] = Nonereturn_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = Nonedata_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension] = <ChannelDimension.FIRST: 'channels_first'>input_data_format: typing.Union[transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension, str, NoneType] = None**kwargs )
Parameters
images (
ImageInput) — Image to preprocess. Expects a single or batch of images with pixel values ranging from 0 to 255. If passing in images with pixel values between 0 and 1, setdo_rescale=False.trimaps (
ImageInput) — Trimap to preprocess.do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_rescale) — Whether to rescale the image values between [0 - 1].rescale_factor (
float, optional, defaults toself.rescale_factor) — Rescale factor to rescale the image by ifdo_rescaleis set toTrue.do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_normalize) — Whether to normalize the image.image_mean (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toself.image_mean) — Image mean to use ifdo_normalizeis set toTrue.image_std (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toself.image_std) — Image standard deviation to use ifdo_normalizeis set toTrue.do_pad (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_pad) — Whether to pad the image.size_divisibility (
int, optional, defaults toself.size_divisibility) — The size divisibility to pad the image to ifdo_padis set toTrue.return_tensors (
strorTensorType, optional) — The type of tensors to return. Can be one of:Unset: Return a list of
np.ndarray.TensorType.TENSORFLOWor'tf': Return a batch of typetf.Tensor.TensorType.PYTORCHor'pt': Return a batch of typetorch.Tensor.TensorType.NUMPYor'np': Return a batch of typenp.ndarray.TensorType.JAXor'jax': Return a batch of typejax.numpy.ndarray.
data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional, defaults toChannelDimension.FIRST) — The channel dimension format for the output image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format.Unset: Use the channel dimension format of the input image.
input_data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional) — The channel dimension format for the input image. If unset, the channel dimension format is inferred from the input image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format."none"orChannelDimension.NONE: image in (height, width) format.
Preprocess an image or batch of images.
VitMatteForImageMatting
class transformers.VitMatteForImageMatting
( config )
Parameters
This model is a PyTorch [torch.nn.Module](https —//pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.Module) sub-class. Use
it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and — behavior. — config (UperNetConfig): Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
ViTMatte framework leveraging any vision backbone e.g. for ADE20k, CityScapes.
forward
( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Noneoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonelabels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.vitmatte.modeling_vitmatte.ImageMattingOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See VitMatteImageProcessor.call() for details.output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers in case the backbone has them. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers of the backbone. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, height, width), optional) — Ground truth image matting for computing the loss.
Returns
transformers.models.vitmatte.modeling_vitmatte.ImageMattingOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.vitmatte.modeling_vitmatte.ImageMattingOutput or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (VitMatteConfig) and inputs.
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Loss.alphas (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Estimated alpha values.hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the model at the output of each stage.attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, patch_size, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The VitMatteForImageMatting forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Copied
Last updated