CLIPSeg
CLIPSeg
Overview
The CLIPSeg model was proposed in Image Segmentation Using Text and Image Prompts by Timo Lüddecke and Alexander Ecker. CLIPSeg adds a minimal decoder on top of a frozen CLIP model for zero- and one-shot image segmentation.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
Image segmentation is usually addressed by training a model for a fixed set of object classes. Incorporating additional classes or more complex queries later is expensive as it requires re-training the model on a dataset that encompasses these expressions. Here we propose a system that can generate image segmentations based on arbitrary prompts at test time. A prompt can be either a text or an image. This approach enables us to create a unified model (trained once) for three common segmentation tasks, which come with distinct challenges: referring expression segmentation, zero-shot segmentation and one-shot segmentation. We build upon the CLIP model as a backbone which we extend with a transformer-based decoder that enables dense prediction. After training on an extended version of the PhraseCut dataset, our system generates a binary segmentation map for an image based on a free-text prompt or on an additional image expressing the query. We analyze different variants of the latter image-based prompts in detail. This novel hybrid input allows for dynamic adaptation not only to the three segmentation tasks mentioned above, but to any binary segmentation task where a text or image query can be formulated. Finally, we find our system to adapt well to generalized queries involving affordances or properties
Tips:
CLIPSegForImageSegmentation adds a decoder on top of CLIPSegModel. The latter is identical to CLIPModel.
CLIPSegForImageSegmentation can generate image segmentations based on arbitrary prompts at test time. A prompt can be either a text (provided to the model as
input_ids) or an image (provided to the model asconditional_pixel_values). One can also provide custom conditional embeddings (provided to the model asconditional_embeddings).
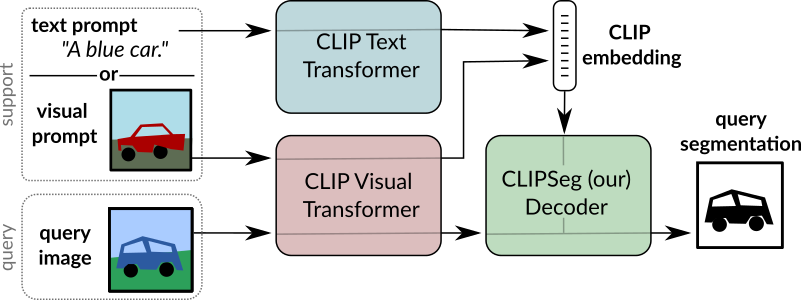
CLIPSeg overview. Taken from the original paper.
This model was contributed by nielsr. The original code can be found here.
Resources
A list of official BOINC AI and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with CLIPSeg. If you’re interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we’ll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
Image Segmentation
A notebook that illustrates zero-shot image segmentation with CLIPSeg.
CLIPSegConfig
class transformers.CLIPSegConfig
( text_config = Nonevision_config = Noneprojection_dim = 512logit_scale_init_value = 2.6592extract_layers = [3, 6, 9]reduce_dim = 64decoder_num_attention_heads = 4decoder_attention_dropout = 0.0decoder_hidden_act = 'quick_gelu'decoder_intermediate_size = 2048conditional_layer = 0use_complex_transposed_convolution = False**kwargs )
Parameters
text_config (
dict, optional) — Dictionary of configuration options used to initialize CLIPSegTextConfig.vision_config (
dict, optional) — Dictionary of configuration options used to initialize CLIPSegVisionConfig.projection_dim (
int, optional, defaults to 512) — Dimensionality of text and vision projection layers.logit_scale_init_value (
float, optional, defaults to 2.6592) — The inital value of the logit_scale paramter. Default is used as per the original CLIPSeg implementation.extract_layers (
List[int], optional, defaults to [3, 6, 9]) — Layers to extract when forwarding the query image through the frozen visual backbone of CLIP.reduce_dim (
int, optional, defaults to 64) — Dimensionality to reduce the CLIP vision embedding.decoder_num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 4) — Number of attention heads in the decoder of CLIPSeg.decoder_attention_dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout ratio for the attention probabilities.decoder_hidden_act (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"quick_gelu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new"`"quick_gelu"are supported.decoder_intermediate_size (
int, optional, defaults to 2048) — Dimensionality of the “intermediate” (i.e., feed-forward) layers in the Transformer decoder.conditional_layer (
int, optional, defaults to 0) — The layer to use of the Transformer encoder whose activations will be combined with the condition embeddings using FiLM (Feature-wise Linear Modulation). If 0, the last layer is used.use_complex_transposed_convolution (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to use a more complex transposed convolution in the decoder, enabling more fine-grained segmentation.kwargs (optional) — Dictionary of keyword arguments.
CLIPSegConfig is the configuration class to store the configuration of a CLIPSegModel. It is used to instantiate a CLIPSeg model according to the specified arguments, defining the text model and vision model configs. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the CLIPSeg CIDAS/clipseg-rd64 architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
Copied
from_text_vision_configs
( text_config: CLIPSegTextConfigvision_config: CLIPSegVisionConfig**kwargs ) → CLIPSegConfig
Returns
An instance of a configuration object
Instantiate a CLIPSegConfig (or a derived class) from clipseg text model configuration and clipseg vision model configuration.
CLIPSegTextConfig
class transformers.CLIPSegTextConfig
( vocab_size = 49408hidden_size = 512intermediate_size = 2048num_hidden_layers = 12num_attention_heads = 8max_position_embeddings = 77hidden_act = 'quick_gelu'layer_norm_eps = 1e-05attention_dropout = 0.0initializer_range = 0.02initializer_factor = 1.0pad_token_id = 1bos_token_id = 49406eos_token_id = 49407**kwargs )
Parameters
vocab_size (
int, optional, defaults to 49408) — Vocabulary size of the CLIPSeg text model. Defines the number of different tokens that can be represented by theinputs_idspassed when calling CLIPSegModel.hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 512) — Dimensionality of the encoder layers and the pooler layer.intermediate_size (
int, optional, defaults to 2048) — Dimensionality of the “intermediate” (i.e., feed-forward) layer in the Transformer encoder.num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of hidden layers in the Transformer encoder.num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 8) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the Transformer encoder.max_position_embeddings (
int, optional, defaults to 77) — The maximum sequence length that this model might ever be used with. Typically set this to something large just in case (e.g., 512 or 1024 or 2048).hidden_act (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"quick_gelu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new"`"quick_gelu"are supported.layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-5) — The epsilon used by the layer normalization layers.attention_dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout ratio for the attention probabilities.initializer_range (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices.initializer_factor (`float“, optional, defaults to 1) — A factor for initializing all weight matrices (should be kept to 1, used internally for initialization testing).
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a CLIPSegModel. It is used to instantiate an CLIPSeg model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the CLIPSeg CIDAS/clipseg-rd64 architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
Copied
CLIPSegVisionConfig
class transformers.CLIPSegVisionConfig
( hidden_size = 768intermediate_size = 3072num_hidden_layers = 12num_attention_heads = 12num_channels = 3image_size = 224patch_size = 32hidden_act = 'quick_gelu'layer_norm_eps = 1e-05attention_dropout = 0.0initializer_range = 0.02initializer_factor = 1.0**kwargs )
Parameters
hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 768) — Dimensionality of the encoder layers and the pooler layer.intermediate_size (
int, optional, defaults to 3072) — Dimensionality of the “intermediate” (i.e., feed-forward) layer in the Transformer encoder.num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of hidden layers in the Transformer encoder.num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the Transformer encoder.image_size (
int, optional, defaults to 224) — The size (resolution) of each image.patch_size (
int, optional, defaults to 32) — The size (resolution) of each patch.hidden_act (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"quick_gelu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new"`"quick_gelu"are supported.layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-5) — The epsilon used by the layer normalization layers.attention_dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout ratio for the attention probabilities.initializer_range (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices.initializer_factor (`float“, optional, defaults to 1) — A factor for initializing all weight matrices (should be kept to 1, used internally for initialization testing).
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a CLIPSegModel. It is used to instantiate an CLIPSeg model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the CLIPSeg CIDAS/clipseg-rd64 architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
Copied
CLIPSegProcessor
class transformers.CLIPSegProcessor
( image_processor = Nonetokenizer = None**kwargs )
Parameters
image_processor (ViTImageProcessor) — The image processor is a required input.
tokenizer (CLIPTokenizerFast) — The tokenizer is a required input.
Constructs a CLIPSeg processor which wraps a CLIPSeg image processor and a CLIP tokenizer into a single processor.
CLIPSegProcessor offers all the functionalities of ViTImageProcessor and CLIPTokenizerFast. See the __call__() and decode() for more information.
batch_decode
( *args**kwargs )
This method forwards all its arguments to CLIPTokenizerFast’s batch_decode(). Please refer to the docstring of this method for more information.
decode
( *args**kwargs )
This method forwards all its arguments to CLIPTokenizerFast’s decode(). Please refer to the docstring of this method for more information.
CLIPSegModel
class transformers.CLIPSegModel
( config: CLIPSegConfig )
Parameters
config (CLIPSegConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = Nonepixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = Noneattention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Noneposition_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = Nonereturn_loss: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.clipseg.modeling_clipseg.CLIPSegOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. See PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() and PreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details.
attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:1 for tokens that are not masked,
0 for tokens that are masked.
position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1].pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See CLIPImageProcessor.call() for details.return_loss (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the contrastive loss.output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.models.clipseg.modeling_clipseg.CLIPSegOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.clipseg.modeling_clipseg.CLIPSegOutput or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.clipseg.configuration_clipseg.CLIPSegConfig'>) and inputs.
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenreturn_lossisTrue) — Contrastive loss for image-text similarity.logits_per_image:(
torch.FloatTensorof shape(image_batch_size, text_batch_size)) — The scaled dot product scores betweenimage_embedsandtext_embeds. This represents the image-text similarity scores.logits_per_text:(
torch.FloatTensorof shape(text_batch_size, image_batch_size)) — The scaled dot product scores betweentext_embedsandimage_embeds. This represents the text-image similarity scores.text_embeds(
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, output_dim) — The text embeddings obtained by applying the projection layer to the pooled output of CLIPSegTextModel.image_embeds(
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, output_dim) — The image embeddings obtained by applying the projection layer to the pooled output of CLIPSegVisionModel.text_model_output(
BaseModelOutputWithPooling): The output of the CLIPSegTextModel.vision_model_output(
BaseModelOutputWithPooling): The output of the CLIPSegVisionModel.
The CLIPSegModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Copied
get_text_features
( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Noneattention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Noneposition_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Noneoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → text_features (torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, output_dim)
Parameters
input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. See PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() and PreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details.
attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:1 for tokens that are not masked,
0 for tokens that are masked.
position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1].output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
text_features (torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, output_dim)
The text embeddings obtained by applying the projection layer to the pooled output of CLIPSegTextModel.
The CLIPSegModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Copied
get_image_features
( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = Noneoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → image_features (torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, output_dim)
Parameters
pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See CLIPImageProcessor.call() for details.output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
image_features (torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, output_dim)
The image embeddings obtained by applying the projection layer to the pooled output of CLIPSegVisionModel.
The CLIPSegModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Copied
CLIPSegTextModel
class transformers.CLIPSegTextModel
( config: CLIPSegTextConfig )
forward
( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Noneattention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Noneposition_ids: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Noneoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. See PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() and PreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details.
attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:1 for tokens that are not masked,
0 for tokens that are masked.
position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1].output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.clipseg.configuration_clipseg.CLIPSegTextConfig'>) and inputs.
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model.pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Last layer hidden-state of the first token of the sequence (classification token) after further processing through the layers used for the auxiliary pretraining task. E.g. for BERT-family of models, this returns the classification token after processing through a linear layer and a tanh activation function. The linear layer weights are trained from the next sentence prediction (classification) objective during pretraining.hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The CLIPSegTextModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Copied
CLIPSegVisionModel
class transformers.CLIPSegVisionModel
( config: CLIPSegVisionConfig )
forward
( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = Noneoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See CLIPImageProcessor.call() for details.output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPooling or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.clipseg.configuration_clipseg.CLIPSegVisionConfig'>) and inputs.
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model.pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Last layer hidden-state of the first token of the sequence (classification token) after further processing through the layers used for the auxiliary pretraining task. E.g. for BERT-family of models, this returns the classification token after processing through a linear layer and a tanh activation function. The linear layer weights are trained from the next sentence prediction (classification) objective during pretraining.hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The CLIPSegVisionModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Copied
CLIPSegForImageSegmentation
class transformers.CLIPSegForImageSegmentation
( config: CLIPSegConfig )
Parameters
config (CLIPSegConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
CLIPSeg model with a Transformer-based decoder on top for zero-shot and one-shot image segmentation.
This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( input_ids: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = Nonepixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = Noneconditional_pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = Noneconditional_embeddings: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = Noneattention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Noneposition_ids: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = Nonelabels: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = Noneoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.clipseg.modeling_clipseg.CLIPSegImageSegmentationOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
input_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.Indices can be obtained using AutoTokenizer. See PreTrainedTokenizer.encode() and PreTrainedTokenizer.call() for details.
attention_mask (
torch.Tensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:1 for tokens that are not masked,
0 for tokens that are masked.
position_ids (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1].pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See CLIPImageProcessor.call() for details.return_loss (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the contrastive loss.output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — Labels for computing the sequence classification/regression loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels == 1a regression loss is computed (Mean-Square loss), Ifconfig.num_labels > 1a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
Returns
transformers.models.clipseg.modeling_clipseg.CLIPSegImageSegmentationOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.clipseg.modeling_clipseg.CLIPSegImageSegmentationOutput or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.clipseg.configuration_clipseg.CLIPSegTextConfig'>) and inputs.
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenreturn_lossisTrue) — Contrastive loss for image-text similarity. …vision_model_output (
BaseModelOutputWithPooling) — The output of the CLIPSegVisionModel.
The CLIPSegForImageSegmentation forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Copied
Last updated