VideoMAE
VideoMAE
Overview
The VideoMAE model was proposed in VideoMAE: Masked Autoencoders are Data-Efficient Learners for Self-Supervised Video Pre-Training by Zhan Tong, Yibing Song, Jue Wang, Limin Wang. VideoMAE extends masked auto encoders (MAE) to video, claiming state-of-the-art performance on several video classification benchmarks.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
Pre-training video transformers on extra large-scale datasets is generally required to achieve premier performance on relatively small datasets. In this paper, we show that video masked autoencoders (VideoMAE) are data-efficient learners for self-supervised video pre-training (SSVP). We are inspired by the recent ImageMAE and propose customized video tube masking and reconstruction. These simple designs turn out to be effective for overcoming information leakage caused by the temporal correlation during video reconstruction. We obtain three important findings on SSVP: (1) An extremely high proportion of masking ratio (i.e., 90% to 95%) still yields favorable performance of VideoMAE. The temporally redundant video content enables higher masking ratio than that of images. (2) VideoMAE achieves impressive results on very small datasets (i.e., around 3k-4k videos) without using any extra data. This is partially ascribed to the challenging task of video reconstruction to enforce high-level structure learning. (3) VideoMAE shows that data quality is more important than data quantity for SSVP. Domain shift between pre-training and target datasets are important issues in SSVP. Notably, our VideoMAE with the vanilla ViT backbone can achieve 83.9% on Kinects-400, 75.3% on Something-Something V2, 90.8% on UCF101, and 61.1% on HMDB51 without using any extra data.
Tips:
One can use VideoMAEImageProcessor to prepare videos for the model. It will resize + normalize all frames of a video for you.
VideoMAEForPreTraining includes the decoder on top for self-supervised pre-training.
VideoMAE pre-training. Taken from the original paper.
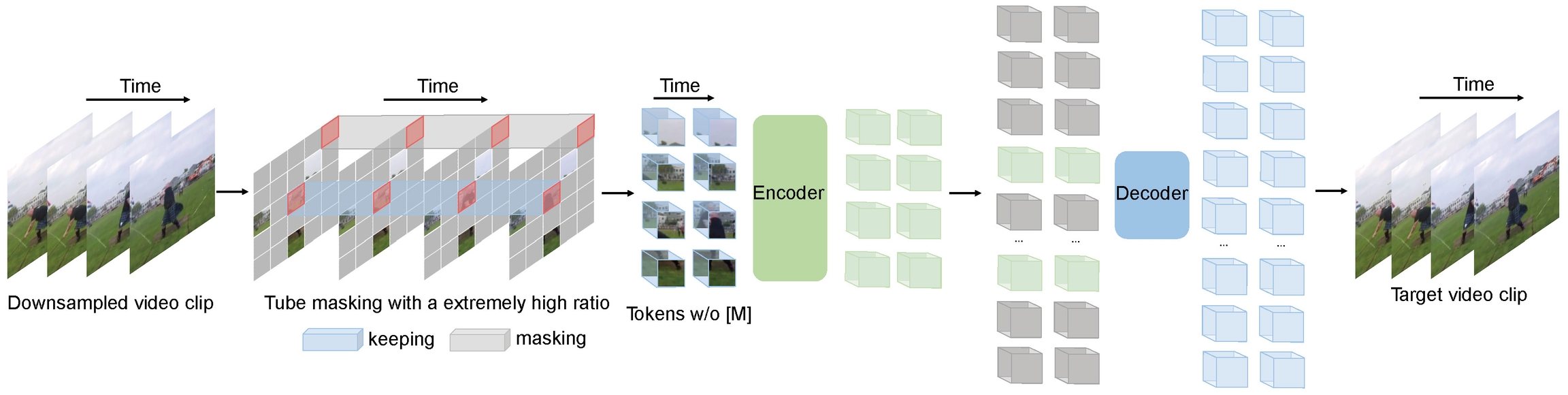
This model was contributed by nielsr. The original code can be found here.
Resources
A list of official BOINC AI and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with VideoMAE. If you’re interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we’ll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
Video classification
A notebook that shows how to fine-tune a VideoMAE model on a custom dataset.
VideoMAEConfig
class transformers.VideoMAEConfig
( image_size = 224patch_size = 16num_channels = 3num_frames = 16tubelet_size = 2hidden_size = 768num_hidden_layers = 12num_attention_heads = 12intermediate_size = 3072hidden_act = 'gelu'hidden_dropout_prob = 0.0attention_probs_dropout_prob = 0.0initializer_range = 0.02layer_norm_eps = 1e-12qkv_bias = Trueuse_mean_pooling = Truedecoder_num_attention_heads = 6decoder_hidden_size = 384decoder_num_hidden_layers = 4decoder_intermediate_size = 1536norm_pix_loss = True**kwargs )
Parameters
image_size (
int, optional, defaults to 224) — The size (resolution) of each image.patch_size (
int, optional, defaults to 16) — The size (resolution) of each patch.num_channels (
int, optional, defaults to 3) — The number of input channels.num_frames (
int, optional, defaults to 16) — The number of frames in each video.tubelet_size (
int, optional, defaults to 2) — The number of tubelets.hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 768) — Dimensionality of the encoder layers and the pooler layer.num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of hidden layers in the Transformer encoder.num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the Transformer encoder.intermediate_size (
int, optional, defaults to 3072) — Dimensionality of the “intermediate” (i.e., feed-forward) layer in the Transformer encoder.hidden_act (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"gelu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new"are supported.hidden_dropout_prob (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout probabilitiy for all fully connected layers in the embeddings, encoder, and pooler.attention_probs_dropout_prob (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout ratio for the attention probabilities.initializer_range (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices.layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-12) — The epsilon used by the layer normalization layers.qkv_bias (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to add a bias to the queries, keys and values.use_mean_pooling (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to mean pool the final hidden states instead of using the final hidden state of the [CLS] token.decoder_num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 6) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the decoder.decoder_hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 384) — Dimensionality of the decoder.decoder_num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 4) — Number of hidden layers in the decoder.decoder_intermediate_size (
int, optional, defaults to 1536) — Dimensionality of the “intermediate” (i.e., feed-forward) layer in the decoder.norm_pix_loss (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to normalize the target patch pixels.
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a VideoMAEModel. It is used to instantiate a VideoMAE model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the VideoMAE MCG-NJU/videomae-base architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
Copied
VideoMAEFeatureExtractor
class transformers.VideoMAEFeatureExtractor
( *args**kwargs )
__call__
( images**kwargs )
Preprocess an image or a batch of images.
VideoMAEImageProcessor
class transformers.VideoMAEImageProcessor
( do_resize: bool = Truesize: typing.Dict[str, int] = Noneresample: Resampling = <Resampling.BILINEAR: 2>do_center_crop: bool = Truecrop_size: typing.Dict[str, int] = Nonedo_rescale: bool = Truerescale_factor: typing.Union[int, float] = 0.00392156862745098do_normalize: bool = Trueimage_mean: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = Noneimage_std: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = None**kwargs )
Parameters
do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to resize the image’s (height, width) dimensions to the specifiedsize. Can be overridden by thedo_resizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod.size (
Dict[str, int]optional, defaults to{"shortest_edge" -- 224}): Size of the output image after resizing. The shortest edge of the image will be resized tosize["shortest_edge"]while maintaining the aspect ratio of the original image. Can be overriden bysizein thepreprocessmethod.resample (
PILImageResampling, optional, defaults toPILImageResampling.BILINEAR) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. Can be overridden by theresampleparameter in thepreprocessmethod.do_center_crop (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to center crop the image to the specifiedcrop_size. Can be overridden by thedo_center_cropparameter in thepreprocessmethod.crop_size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults to{"height" -- 224, "width": 224}): Size of the image after applying the center crop. Can be overridden by thecrop_sizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod.do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to rescale the image by the specified scalerescale_factor. Can be overridden by thedo_rescaleparameter in thepreprocessmethod.rescale_factor (
intorfloat, optional, defaults to1/255) — Defines the scale factor to use if rescaling the image. Can be overridden by therescale_factorparameter in thepreprocessmethod.do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to normalize the image. Can be overridden by thedo_normalizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod.image_mean (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_STANDARD_MEAN) — Mean to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats the length of the number of channels in the image. Can be overridden by theimage_meanparameter in thepreprocessmethod.image_std (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_STANDARD_STD) — Standard deviation to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats the length of the number of channels in the image. Can be overridden by theimage_stdparameter in thepreprocessmethod.
Constructs a VideoMAE image processor.
preprocess
( videos: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), typing.List[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image')], typing.List[numpy.ndarray], typing.List[ForwardRef('torch.Tensor')]]do_resize: bool = Nonesize: typing.Dict[str, int] = Noneresample: Resampling = Nonedo_center_crop: bool = Nonecrop_size: typing.Dict[str, int] = Nonedo_rescale: bool = Nonerescale_factor: float = Nonedo_normalize: bool = Noneimage_mean: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = Noneimage_std: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = Nonereturn_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = Nonedata_format: ChannelDimension = <ChannelDimension.FIRST: 'channels_first'>input_data_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension, NoneType] = None**kwargs )
Parameters
images (
ImageInput) — Image to preprocess. Expects a single or batch of images with pixel values ranging from 0 to 255. If passing in images with pixel values between 0 and 1, setdo_rescale=False.do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_resize) — Whether to resize the image.size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.size) — Size of the image after applying resize.resample (
PILImageResampling, optional, defaults toself.resample) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. This can be one of the enumPILImageResampling, Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue.do_center_crop (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_centre_crop) — Whether to centre crop the image.crop_size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.crop_size) — Size of the image after applying the centre crop.do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_rescale) — Whether to rescale the image values between [0 - 1].rescale_factor (
float, optional, defaults toself.rescale_factor) — Rescale factor to rescale the image by ifdo_rescaleis set toTrue.do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_normalize) — Whether to normalize the image.image_mean (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toself.image_mean) — Image mean.image_std (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toself.image_std) — Image standard deviation.return_tensors (
strorTensorType, optional) — The type of tensors to return. Can be one of:Unset: Return a list of
np.ndarray.TensorType.TENSORFLOWor'tf': Return a batch of typetf.Tensor.TensorType.PYTORCHor'pt': Return a batch of typetorch.Tensor.TensorType.NUMPYor'np': Return a batch of typenp.ndarray.TensorType.JAXor'jax': Return a batch of typejax.numpy.ndarray.
data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional, defaults toChannelDimension.FIRST) — The channel dimension format for the output image. Can be one of:ChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format.ChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format.Unset: Use the inferred channel dimension format of the input image.
input_data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional) — The channel dimension format for the input image. If unset, the channel dimension format is inferred from the input image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format."none"orChannelDimension.NONE: image in (height, width) format.
Preprocess an image or batch of images.
VideoMAEModel
class transformers.VideoMAEModel
( config )
Parameters
config (VideoMAEConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The bare VideoMAE Model transformer outputting raw hidden-states without any specific head on top. This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( pixel_values: FloatTensorbool_masked_pos: typing.Optional[torch.BoolTensor] = Nonehead_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Noneoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_frames, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See VideoMAEImageProcessor.call() for details.head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:1 indicates the head is not masked,
0 indicates the head is masked.
output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.bool_masked_pos (
torch.BoolTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length), optional) — Boolean masked positions. Indicates which patches are masked (1) and which aren’t (0). Each video in the batch must have the same number of masked patches. IfNone, then all patches are considered. Sequence length is(num_frames // tubelet_size) * (image_size // patch_size) ** 2.
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutput or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (VideoMAEConfig) and inputs.
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model.hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The VideoMAEModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Copied
VideoMAEForPreTraining
class transformers.VideoMAEForPreTraining
( config )
Parameters
config (VideoMAEConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The VideoMAE Model transformer with the decoder on top for self-supervised pre-training. This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( pixel_values: FloatTensorbool_masked_pos: BoolTensorhead_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Noneoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.videomae.modeling_videomae.VideoMAEForPreTrainingOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_frames, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See VideoMAEImageProcessor.call() for details.head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:1 indicates the head is not masked,
0 indicates the head is masked.
output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.bool_masked_pos (
torch.BoolTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length)) — Boolean masked positions. Indicates which patches are masked (1) and which aren’t (0). Each video in the batch must have the same number of masked patches. Sequence length is(num_frames // tubelet_size) * (image_size // patch_size) ** 2.
Returns
transformers.models.videomae.modeling_videomae.VideoMAEForPreTrainingOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.videomae.modeling_videomae.VideoMAEForPreTrainingOutput or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (VideoMAEConfig) and inputs.
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,)) — Pixel reconstruction loss.logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, patch_size ** 2 * num_channels)) — Pixel reconstruction logits.hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length). Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The VideoMAEForPreTraining forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Copied
VideoMAEForVideoClassification
class transformers.VideoMAEForVideoClassification
( config )
Parameters
config (VideoMAEConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
VideoMAE Model transformer with a video classification head on top (a linear layer on top of the average pooled hidden states of all tokens) e.g. for ImageNet. This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Nonehead_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Nonelabels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Noneoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_frames, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See VideoMAEImageProcessor.call() for details.head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:1 indicates the head is not masked,
0 indicates the head is masked.
output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — Labels for computing the image classification/regression loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels == 1a regression loss is computed (Mean-Square loss), Ifconfig.num_labels > 1a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutput or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (VideoMAEConfig) and inputs.
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) loss.logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) scores (before SoftMax).hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the model at the output of each stage.attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, patch_size, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The VideoMAEForVideoClassification forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Copied
Last updated