BEiT
BEiT
Overview
The BEiT model was proposed in BEiT: BERT Pre-Training of Image Transformers by Hangbo Bao, Li Dong and Furu Wei. Inspired by BERT, BEiT is the first paper that makes self-supervised pre-training of Vision Transformers (ViTs) outperform supervised pre-training. Rather than pre-training the model to predict the class of an image (as done in the original ViT paper), BEiT models are pre-trained to predict visual tokens from the codebook of OpenAI’s DALL-E model given masked patches.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
We introduce a self-supervised vision representation model BEiT, which stands for Bidirectional Encoder representation from Image Transformers. Following BERT developed in the natural language processing area, we propose a masked image modeling task to pretrain vision Transformers. Specifically, each image has two views in our pre-training, i.e, image patches (such as 16x16 pixels), and visual tokens (i.e., discrete tokens). We first “tokenize” the original image into visual tokens. Then we randomly mask some image patches and fed them into the backbone Transformer. The pre-training objective is to recover the original visual tokens based on the corrupted image patches. After pre-training BEiT, we directly fine-tune the model parameters on downstream tasks by appending task layers upon the pretrained encoder. Experimental results on image classification and semantic segmentation show that our model achieves competitive results with previous pre-training methods. For example, base-size BEiT achieves 83.2% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1K, significantly outperforming from-scratch DeiT training (81.8%) with the same setup. Moreover, large-size BEiT obtains 86.3% only using ImageNet-1K, even outperforming ViT-L with supervised pre-training on ImageNet-22K (85.2%).
Tips:
BEiT models are regular Vision Transformers, but pre-trained in a self-supervised way rather than supervised. They outperform both the original model (ViT) as well as Data-efficient Image Transformers (DeiT) when fine-tuned on ImageNet-1K and CIFAR-100. You can check out demo notebooks regarding inference as well as fine-tuning on custom data here (you can just replace ViTFeatureExtractor by BeitImageProcessor and ViTForImageClassification by BeitForImageClassification).
There’s also a demo notebook available which showcases how to combine DALL-E’s image tokenizer with BEiT for performing masked image modeling. You can find it here.
As the BEiT models expect each image to be of the same size (resolution), one can use BeitImageProcessor to resize (or rescale) and normalize images for the model.
Both the patch resolution and image resolution used during pre-training or fine-tuning are reflected in the name of each checkpoint. For example,
microsoft/beit-base-patch16-224refers to a base-sized architecture with patch resolution of 16x16 and fine-tuning resolution of 224x224. All checkpoints can be found on the hub.The available checkpoints are either (1) pre-trained on ImageNet-22k (a collection of 14 million images and 22k classes) only, (2) also fine-tuned on ImageNet-22k or (3) also fine-tuned on ImageNet-1k (also referred to as ILSVRC 2012, a collection of 1.3 million images and 1,000 classes).
BEiT uses relative position embeddings, inspired by the T5 model. During pre-training, the authors shared the relative position bias among the several self-attention layers. During fine-tuning, each layer’s relative position bias is initialized with the shared relative position bias obtained after pre-training. Note that, if one wants to pre-train a model from scratch, one needs to either set the
use_relative_position_biasor theuse_relative_position_biasattribute of BeitConfig toTruein order to add position embeddings.
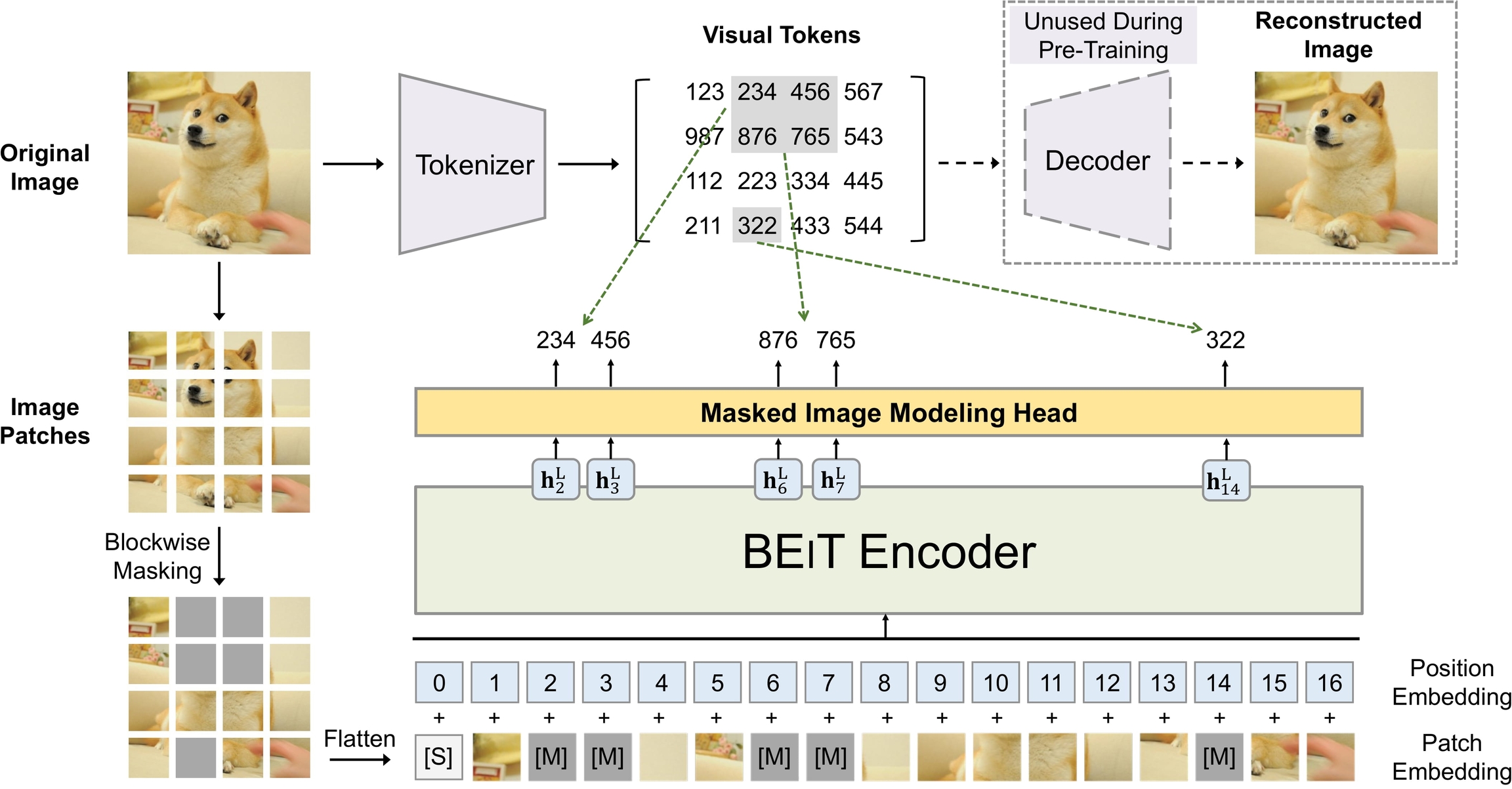
BEiT pre-training. Taken from the original paper.
This model was contributed by nielsr. The JAX/FLAX version of this model was contributed by kamalkraj. The original code can be found here.
Resources
A list of official BOINC AI and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with BEiT.
Image Classification
BeitForImageClassification is supported by this example script and notebook.
See also: Image classification task guide
Semantic segmentation
If you’re interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we’ll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
BEiT specific outputs
class transformers.models.beit.modeling_beit.BeitModelOutputWithPooling
( last_hidden_state: FloatTensor = Nonepooler_output: FloatTensor = Nonehidden_states: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = Noneattentions: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]] = None )
Parameters
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model.pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Average of the last layer hidden states of the patch tokens (excluding the [CLS] token) if config.use_mean_pooling is set to True. If set to False, then the final hidden state of the [CLS] token will be returned.hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
Class for outputs of BeitModel.
class transformers.models.beit.modeling_flax_beit.FlaxBeitModelOutputWithPooling
( last_hidden_state: Array = Nonepooler_output: Array = Nonehidden_states: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[jax.Array]] = Noneattentions: typing.Optional[typing.Tuple[jax.Array]] = None )
Parameters
last_hidden_state (
jnp.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model.pooler_output (
jnp.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Average of the last layer hidden states of the patch tokens (excluding the [CLS] token) if config.use_mean_pooling is set to True. If set to False, then the final hidden state of the [CLS] token will be returned.hidden_states (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.attentions (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length). Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
Class for outputs of FlaxBeitModel.
BeitConfig
class transformers.BeitConfig
( vocab_size = 8192hidden_size = 768num_hidden_layers = 12num_attention_heads = 12intermediate_size = 3072hidden_act = 'gelu'hidden_dropout_prob = 0.0attention_probs_dropout_prob = 0.0initializer_range = 0.02layer_norm_eps = 1e-12image_size = 224patch_size = 16num_channels = 3use_mask_token = Falseuse_absolute_position_embeddings = Falseuse_relative_position_bias = Falseuse_shared_relative_position_bias = Falselayer_scale_init_value = 0.1drop_path_rate = 0.1use_mean_pooling = Trueout_indices = [3, 5, 7, 11]pool_scales = [1, 2, 3, 6]use_auxiliary_head = Trueauxiliary_loss_weight = 0.4auxiliary_channels = 256auxiliary_num_convs = 1auxiliary_concat_input = Falsesemantic_loss_ignore_index = 255**kwargs )
Parameters
vocab_size (
int, optional, defaults to 8092) — Vocabulary size of the BEiT model. Defines the number of different image tokens that can be used during pre-training.hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 768) — Dimensionality of the encoder layers and the pooler layer.num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of hidden layers in the Transformer encoder.num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the Transformer encoder.intermediate_size (
int, optional, defaults to 3072) — Dimensionality of the “intermediate” (i.e., feed-forward) layer in the Transformer encoder.hidden_act (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"gelu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new"are supported.hidden_dropout_prob (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout probability for all fully connected layers in the embeddings, encoder, and pooler.attention_probs_dropout_prob (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout ratio for the attention probabilities.initializer_range (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices.layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-12) — The epsilon used by the layer normalization layers.image_size (
int, optional, defaults to 224) — The size (resolution) of each image.patch_size (
int, optional, defaults to 16) — The size (resolution) of each patch.num_channels (
int, optional, defaults to 3) — The number of input channels.use_mask_token (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to use a mask token for masked image modeling.use_absolute_position_embeddings (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to use BERT-style absolute position embeddings.use_relative_position_bias (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to use T5-style relative position embeddings in the self-attention layers.use_shared_relative_position_bias (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to use the same relative position embeddings across all self-attention layers of the Transformer.layer_scale_init_value (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — Scale to use in the self-attention layers. 0.1 for base, 1e-5 for large. Set 0 to disable layer scale.drop_path_rate (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — Stochastic depth rate per sample (when applied in the main path of residual layers).use_mean_pooling (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to mean pool the final hidden states of the patches instead of using the final hidden state of the CLS token, before applying the classification head.out_indices (
List[int], optional, defaults to[3, 5, 7, 11]) — Indices of the feature maps to use for semantic segmentation.pool_scales (
Tuple[int], optional, defaults to[1, 2, 3, 6]) — Pooling scales used in Pooling Pyramid Module applied on the last feature map.use_auxiliary_head (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to use an auxiliary head during training.auxiliary_loss_weight (
float, optional, defaults to 0.4) — Weight of the cross-entropy loss of the auxiliary head.auxiliary_channels (
int, optional, defaults to 256) — Number of channels to use in the auxiliary head.auxiliary_num_convs (
int, optional, defaults to 1) — Number of convolutional layers to use in the auxiliary head.auxiliary_concat_input (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to concatenate the output of the auxiliary head with the input before the classification layer.semantic_loss_ignore_index (
int, optional, defaults to 255) — The index that is ignored by the loss function of the semantic segmentation model.
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a BeitModel. It is used to instantiate an BEiT model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the BEiT microsoft/beit-base-patch16-224-pt22k architecture.
Example:
Copied
BeitFeatureExtractor
class transformers.BeitFeatureExtractor
( *args**kwargs )
__call__
( imagessegmentation_maps = None**kwargs )
post_process_semantic_segmentation
( outputstarget_sizes: typing.List[typing.Tuple] = None ) → semantic_segmentation
Parameters
outputs (BeitForSemanticSegmentation) — Raw outputs of the model.
target_sizes (
List[Tuple]of lengthbatch_size, optional) — List of tuples corresponding to the requested final size (height, width) of each prediction. If unset, predictions will not be resized.
Returns
semantic_segmentation
List[torch.Tensor] of length batch_size, where each item is a semantic segmentation map of shape (height, width) corresponding to the target_sizes entry (if target_sizes is specified). Each entry of each torch.Tensor correspond to a semantic class id.
Converts the output of BeitForSemanticSegmentation into semantic segmentation maps. Only supports PyTorch.
BeitImageProcessor
class transformers.BeitImageProcessor
( do_resize: bool = Truesize: typing.Dict[str, int] = Noneresample: Resampling = <Resampling.BICUBIC: 3>do_center_crop: bool = Truecrop_size: typing.Dict[str, int] = Nonerescale_factor: typing.Union[int, float] = 0.00392156862745098do_rescale: bool = Truedo_normalize: bool = Trueimage_mean: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = Noneimage_std: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = Nonedo_reduce_labels: bool = False**kwargs )
Parameters
do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to resize the image’s (height, width) dimensions to the specifiedsize. Can be overridden by thedo_resizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod.size (
Dict[str, int]optional, defaults to{"height" -- 256, "width": 256}): Size of the output image after resizing. Can be overridden by thesizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod.resample (
PILImageResampling, optional, defaults toPILImageResampling.BICUBIC) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. Can be overridden by theresampleparameter in thepreprocessmethod.do_center_crop (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to center crop the image. If the input size is smaller thancrop_sizealong any edge, the image is padded with 0’s and then center cropped. Can be overridden by thedo_center_cropparameter in thepreprocessmethod.crop_size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults to{"height" -- 224, "width": 224}): Desired output size when applying center-cropping. Only has an effect ifdo_center_cropis set toTrue. Can be overridden by thecrop_sizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod.do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to rescale the image by the specified scalerescale_factor. Can be overridden by thedo_rescaleparameter in thepreprocessmethod.rescale_factor (
intorfloat, optional, defaults to1/255) — Scale factor to use if rescaling the image. Can be overridden by therescale_factorparameter in thepreprocessmethod.do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to normalize the image. Can be overridden by thedo_normalizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod.image_mean (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_STANDARD_MEAN) — The mean to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats of length of the number of channels of the image. Can be overridden by theimage_meanparameter in thepreprocessmethod.image_std (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_STANDARD_STD) — The standard deviation to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats of length of the number of channels of the image. Can be overridden by theimage_stdparameter in thepreprocessmethod.do_reduce_labels (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether or not to reduce all label values of segmentation maps by 1. Usually used for datasets where 0 is used for background, and background itself is not included in all classes of a dataset (e.g. ADE20k). The background label will be replaced by 255. Can be overridden by thedo_reduce_labelsparameter in thepreprocessmethod.
Constructs a BEiT image processor.
preprocess
( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), typing.List[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image')], typing.List[numpy.ndarray], typing.List[ForwardRef('torch.Tensor')]]segmentation_maps: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), typing.List[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image')], typing.List[numpy.ndarray], typing.List[ForwardRef('torch.Tensor')], NoneType] = Nonedo_resize: bool = Nonesize: typing.Dict[str, int] = Noneresample: Resampling = Nonedo_center_crop: bool = Nonecrop_size: typing.Dict[str, int] = Nonedo_rescale: bool = Nonerescale_factor: float = Nonedo_normalize: bool = Noneimage_mean: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = Noneimage_std: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = Nonedo_reduce_labels: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = Nonedata_format: ChannelDimension = <ChannelDimension.FIRST: 'channels_first'>input_data_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension, NoneType] = None**kwargs )
Parameters
images (
ImageInput) — Image to preprocess. Expects a single or batch of images with pixel values ranging from 0 to 255. If passing in images with pixel values between 0 and 1, setdo_rescale=False.do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_resize) — Whether to resize the image.size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.size) — Size of the image after resizing.resample (
int, optional, defaults toself.resample) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. This can be one of the enumPILImageResampling, Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue.do_center_crop (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_center_crop) — Whether to center crop the image.crop_size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.crop_size) — Size of the image after center crop. If one edge the image is smaller thancrop_size, it will be padded with zeros and then croppeddo_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_rescale) — Whether to rescale the image values between [0 - 1].rescale_factor (
float, optional, defaults toself.rescale_factor) — Rescale factor to rescale the image by ifdo_rescaleis set toTrue.do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_normalize) — Whether to normalize the image.image_mean (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toself.image_mean) — Image mean.image_std (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toself.image_std) — Image standard deviation.do_reduce_labels (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_reduce_labels) — Whether or not to reduce all label values of segmentation maps by 1. Usually used for datasets where 0 is used for background, and background itself is not included in all classes of a dataset (e.g. ADE20k). The background label will be replaced by 255.return_tensors (
strorTensorType, optional) — The type of tensors to return. Can be one of:Unset: Return a list of
np.ndarray.TensorType.TENSORFLOWor'tf': Return a batch of typetf.Tensor.TensorType.PYTORCHor'pt': Return a batch of typetorch.Tensor.TensorType.NUMPYor'np': Return a batch of typenp.ndarray.TensorType.JAXor'jax': Return a batch of typejax.numpy.ndarray.
data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional, defaults toChannelDimension.FIRST) — The channel dimension format for the output image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format.Unset: Use the channel dimension format of the input image.
input_data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional) — The channel dimension format for the input image. If unset, the channel dimension format is inferred from the input image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format."none"orChannelDimension.NONE: image in (height, width) format.
Preprocess an image or batch of images.
post_process_semantic_segmentation
( outputstarget_sizes: typing.List[typing.Tuple] = None ) → semantic_segmentation
Parameters
outputs (BeitForSemanticSegmentation) — Raw outputs of the model.
target_sizes (
List[Tuple]of lengthbatch_size, optional) — List of tuples corresponding to the requested final size (height, width) of each prediction. If unset, predictions will not be resized.
Returns
semantic_segmentation
List[torch.Tensor] of length batch_size, where each item is a semantic segmentation map of shape (height, width) corresponding to the target_sizes entry (if target_sizes is specified). Each entry of each torch.Tensor correspond to a semantic class id.
Converts the output of BeitForSemanticSegmentation into semantic segmentation maps. Only supports PyTorch.
BeitModel
class transformers.BeitModel
( config: BeitConfigadd_pooling_layer: bool = True )
Parameters
config (BeitConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The bare Beit Model transformer outputting raw hidden-states without any specific head on top. This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Nonebool_masked_pos: typing.Optional[torch.BoolTensor] = Nonehead_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Noneoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.beit.modeling_beit.BeitModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See BeitImageProcessor.call() for details.head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:1 indicates the head is not masked,
0 indicates the head is masked.
output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.bool_masked_pos (
torch.BoolTensorof shape(batch_size, num_patches), optional) — Boolean masked positions. Indicates which patches are masked (1) and which aren’t (0).
Returns
transformers.models.beit.modeling_beit.BeitModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.beit.modeling_beit.BeitModelOutputWithPooling or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (BeitConfig) and inputs.
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model.pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Average of the last layer hidden states of the patch tokens (excluding the [CLS] token) if config.use_mean_pooling is set to True. If set to False, then the final hidden state of the [CLS] token will be returned.hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The BeitModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
Copied
BeitForMaskedImageModeling
class transformers.BeitForMaskedImageModeling
( config: BeitConfig )
Parameters
config (BeitConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
Beit Model transformer with a ‘language’ modeling head on top. BEiT does masked image modeling by predicting visual tokens of a Vector-Quantize Variational Autoencoder (VQ-VAE), whereas other vision models like ViT and DeiT predict RGB pixel values. As a result, this class is incompatible with AutoModelForMaskedImageModeling, so you will need to use BeitForMaskedImageModeling directly if you wish to do masked image modeling with BEiT. This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Nonebool_masked_pos: typing.Optional[torch.BoolTensor] = Nonehead_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Nonelabels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Noneoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.MaskedLMOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See BeitImageProcessor.call() for details.head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:1 indicates the head is not masked,
0 indicates the head is masked.
output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.bool_masked_pos (
torch.BoolTensorof shape(batch_size, num_patches)) — Boolean masked positions. Indicates which patches are masked (1) and which aren’t (0).labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — Labels for computing the image classification/regression loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels == 1a regression loss is computed (Mean-Square loss), Ifconfig.num_labels > 1a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.MaskedLMOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.MaskedLMOutput or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (BeitConfig) and inputs.
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Masked language modeling (MLM) loss.logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)) — Prediction scores of the language modeling head (scores for each vocabulary token before SoftMax).hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The BeitForMaskedImageModeling forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Copied
BeitForImageClassification
class transformers.BeitForImageClassification
( config: BeitConfig )
Parameters
config (BeitConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
Beit Model transformer with an image classification head on top (a linear layer on top of the average of the final hidden states of the patch tokens) e.g. for ImageNet.
This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Nonehead_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Nonelabels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Noneoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See BeitImageProcessor.call() for details.head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:1 indicates the head is not masked,
0 indicates the head is masked.
output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — Labels for computing the image classification/regression loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels == 1a regression loss is computed (Mean-Square loss), Ifconfig.num_labels > 1a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutput or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (BeitConfig) and inputs.
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) loss.logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) scores (before SoftMax).hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the model at the output of each stage.attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, patch_size, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The BeitForImageClassification forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
Copied
BeitForSemanticSegmentation
class transformers.BeitForSemanticSegmentation
( config: BeitConfig )
Parameters
config (BeitConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
Beit Model transformer with a semantic segmentation head on top e.g. for ADE20k, CityScapes.
This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Nonehead_mask: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Nonelabels: typing.Optional[torch.Tensor] = Noneoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.SemanticSegmenterOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See BeitImageProcessor.call() for details.head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:1 indicates the head is not masked,
0 indicates the head is masked.
output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, height, width), optional) — Ground truth semantic segmentation maps for computing the loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels > 1, a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.SemanticSegmenterOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.SemanticSegmenterOutput or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (BeitConfig) and inputs.
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) loss.logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, config.num_labels, logits_height, logits_width)) — Classification scores for each pixel.The logits returned do not necessarily have the same size as the
pixel_valuespassed as inputs. This is to avoid doing two interpolations and lose some quality when a user needs to resize the logits to the original image size as post-processing. You should always check your logits shape and resize as needed.hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, patch_size, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, patch_size, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The BeitForSemanticSegmentation forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Copied
FlaxBeitModel
class transformers.FlaxBeitModel
( config: BeitConfiginput_shape = Noneseed: int = 0dtype: dtype = <class 'jax.numpy.float32'>_do_init: bool = True**kwargs )
Parameters
config (BeitConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
dtype (
jax.numpy.dtype, optional, defaults tojax.numpy.float32) — The data type of the computation. Can be one ofjax.numpy.float32,jax.numpy.float16(on GPUs) andjax.numpy.bfloat16(on TPUs).This can be used to enable mixed-precision training or half-precision inference on GPUs or TPUs. If specified all the computation will be performed with the given
dtype.Note that this only specifies the dtype of the computation and does not influence the dtype of model parameters.
If you wish to change the dtype of the model parameters, see to_fp16() and to_bf16().
The bare Beit Model transformer outputting raw hidden-states without any specific head on top.
This model inherits from FlaxPreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading, saving and converting weights from PyTorch models)
This model is also a Flax Linen flax.linen.Module subclass. Use it as a regular Flax linen Module and refer to the Flax documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
Finally, this model supports inherent JAX features such as:
__call__
( pixel_valuesbool_masked_pos = Noneparams: dict = Nonedropout_rng: PRNGKey = Nonetrain: bool = Falseoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.beit.modeling_flax_beit.FlaxBeitModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Returns
transformers.models.beit.modeling_flax_beit.FlaxBeitModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.beit.modeling_flax_beit.FlaxBeitModelOutputWithPooling or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.beit.configuration_beit.BeitConfig'>) and inputs.
last_hidden_state (
jnp.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model.pooler_output (
jnp.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Average of the last layer hidden states of the patch tokens (excluding the [CLS] token) if config.use_mean_pooling is set to True. If set to False, then the final hidden state of the [CLS] token will be returned.hidden_states (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.attentions (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length). Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The FlaxBeitPreTrainedModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Copied
FlaxBeitForMaskedImageModeling
class transformers.FlaxBeitForMaskedImageModeling
( config: BeitConfiginput_shape = Noneseed: int = 0dtype: dtype = <class 'jax.numpy.float32'>_do_init: bool = True**kwargs )
Parameters
config (BeitConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
dtype (
jax.numpy.dtype, optional, defaults tojax.numpy.float32) — The data type of the computation. Can be one ofjax.numpy.float32,jax.numpy.float16(on GPUs) andjax.numpy.bfloat16(on TPUs).This can be used to enable mixed-precision training or half-precision inference on GPUs or TPUs. If specified all the computation will be performed with the given
dtype.Note that this only specifies the dtype of the computation and does not influence the dtype of model parameters.
If you wish to change the dtype of the model parameters, see to_fp16() and to_bf16().
Beit Model transformer with a ‘language’ modeling head on top (to predict visual tokens).
This model inherits from FlaxPreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading, saving and converting weights from PyTorch models)
This model is also a Flax Linen flax.linen.Module subclass. Use it as a regular Flax linen Module and refer to the Flax documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
Finally, this model supports inherent JAX features such as:
__call__
( pixel_valuesbool_masked_pos = Noneparams: dict = Nonedropout_rng: PRNGKey = Nonetrain: bool = Falseoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxMaskedLMOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Returns
transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxMaskedLMOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxMaskedLMOutput or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.beit.configuration_beit.BeitConfig'>) and inputs.
logits (
jnp.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)) — Prediction scores of the language modeling head (scores for each vocabulary token before SoftMax).hidden_states (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.
attentions (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The FlaxBeitPreTrainedModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
bool_masked_pos (numpy.ndarray of shape (batch_size, num_patches)): Boolean masked positions. Indicates which patches are masked (1) and which aren’t (0).
Examples:
Copied
FlaxBeitForImageClassification
class transformers.FlaxBeitForImageClassification
( config: BeitConfiginput_shape = Noneseed: int = 0dtype: dtype = <class 'jax.numpy.float32'>_do_init: bool = True**kwargs )
Parameters
config (BeitConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
dtype (
jax.numpy.dtype, optional, defaults tojax.numpy.float32) — The data type of the computation. Can be one ofjax.numpy.float32,jax.numpy.float16(on GPUs) andjax.numpy.bfloat16(on TPUs).This can be used to enable mixed-precision training or half-precision inference on GPUs or TPUs. If specified all the computation will be performed with the given
dtype.Note that this only specifies the dtype of the computation and does not influence the dtype of model parameters.
If you wish to change the dtype of the model parameters, see to_fp16() and to_bf16().
Beit Model transformer with an image classification head on top (a linear layer on top of the average of the final hidden states of the patch tokens) e.g. for ImageNet.
This model inherits from FlaxPreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading, saving and converting weights from PyTorch models)
This model is also a Flax Linen flax.linen.Module subclass. Use it as a regular Flax linen Module and refer to the Flax documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
Finally, this model supports inherent JAX features such as:
__call__
( pixel_valuesbool_masked_pos = Noneparams: dict = Nonedropout_rng: PRNGKey = Nonetrain: bool = Falseoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxSequenceClassifierOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Returns
transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxSequenceClassifierOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxSequenceClassifierOutput or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.beit.configuration_beit.BeitConfig'>) and inputs.
logits (
jnp.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) scores (before SoftMax).hidden_states (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.
attentions (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The FlaxBeitPreTrainedModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
Copied
Last updated