Optimization
Optimization
The .optimization module provides:
an optimizer with weight decay fixed that can be used to fine-tuned models, and
several schedules in the form of schedule objects that inherit from
_LRSchedule:a gradient accumulation class to accumulate the gradients of multiple batches
AdamW (PyTorch)
class transformers.AdamW
( params: typing.Iterable[torch.nn.parameter.Parameter]lr: float = 0.001betas: typing.Tuple[float, float] = (0.9, 0.999)eps: float = 1e-06weight_decay: float = 0.0correct_bias: bool = Trueno_deprecation_warning: bool = False )
Parameters
params (
Iterable[nn.parameter.Parameter]) — Iterable of parameters to optimize or dictionaries defining parameter groups.lr (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-3) — The learning rate to use.betas (
Tuple[float,float], optional, defaults to (0.9, 0.999)) — Adam’s betas parameters (b1, b2).eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-6) — Adam’s epsilon for numerical stability.weight_decay (
float, optional, defaults to 0) — Decoupled weight decay to apply.correct_bias (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether or not to correct bias in Adam (for instance, in Bert TF repository they useFalse).no_deprecation_warning (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — A flag used to disable the deprecation warning (set toTrueto disable the warning).
Implements Adam algorithm with weight decay fix as introduced in Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization.
step
( closure: typing.Callable = None )
Parameters
closure (
Callable, optional) — A closure that reevaluates the model and returns the loss.
Performs a single optimization step.
AdaFactor (PyTorch)
class transformers.Adafactor
( paramslr = Noneeps = (1e-30, 0.001)clip_threshold = 1.0decay_rate = -0.8beta1 = Noneweight_decay = 0.0scale_parameter = Truerelative_step = Truewarmup_init = False )
Parameters
params (
Iterable[nn.parameter.Parameter]) — Iterable of parameters to optimize or dictionaries defining parameter groups.lr (
float, optional) — The external learning rate.eps (
Tuple[float, float], optional, defaults to (1e-30, 1e-3)) — Regularization constants for square gradient and parameter scale respectivelyclip_threshold (
float, optional, defaults 1.0) — Threshold of root mean square of final gradient updatedecay_rate (
float, optional, defaults to -0.8) — Coefficient used to compute running averages of squarebeta1 (
float, optional) — Coefficient used for computing running averages of gradientweight_decay (
float, optional, defaults to 0) — Weight decay (L2 penalty)scale_parameter (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — If True, learning rate is scaled by root mean squarerelative_step (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — If True, time-dependent learning rate is computed instead of external learning ratewarmup_init (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Time-dependent learning rate computation depends on whether warm-up initialization is being used
AdaFactor pytorch implementation can be used as a drop in replacement for Adam original fairseq code: https://github.com/pytorch/fairseq/blob/master/fairseq/optim/adafactor.py
Paper: Adafactor: Adaptive Learning Rates with Sublinear Memory Cost https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.04235 Note that this optimizer internally adjusts the learning rate depending on the scale_parameter, relative_step and warmup_init options. To use a manual (external) learning rate schedule you should set scale_parameter=False and relative_step=False.
This implementation handles low-precision (FP16, bfloat) values, but we have not thoroughly tested.
Recommended T5 finetuning settings (https://discuss.boincai.com/t/t5-finetuning-tips/684/3):
Training without LR warmup or clip_threshold is not recommended.
use scheduled LR warm-up to fixed LR
use clip_threshold=1.0 (https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.04235)
Disable relative updates
Use scale_parameter=False
Additional optimizer operations like gradient clipping should not be used alongside Adafactor
Example:
Copied
Others reported the following combination to work well:
Copied
When using lr=None with Trainer you will most likely need to use AdafactorSchedule
scheduler as following:
Copied
Usage:
Copied
step
( closure = None )
Parameters
closure (callable, optional) — A closure that reevaluates the model and returns the loss.
Performs a single optimization step
AdamWeightDecay (TensorFlow)
class transformers.AdamWeightDecay
( learning_rate: typing.Union[float, keras.src.optimizers.schedules.learning_rate_schedule.LearningRateSchedule] = 0.001beta_1: float = 0.9beta_2: float = 0.999epsilon: float = 1e-07amsgrad: bool = Falseweight_decay_rate: float = 0.0include_in_weight_decay: typing.Optional[typing.List[str]] = Noneexclude_from_weight_decay: typing.Optional[typing.List[str]] = Nonename: str = 'AdamWeightDecay'**kwargs )
Parameters
learning_rate (
Union[float, tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.LearningRateSchedule], optional, defaults to 1e-3) — The learning rate to use or a schedule.beta_1 (
float, optional, defaults to 0.9) — The beta1 parameter in Adam, which is the exponential decay rate for the 1st momentum estimates.beta_2 (
float, optional, defaults to 0.999) — The beta2 parameter in Adam, which is the exponential decay rate for the 2nd momentum estimates.epsilon (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-7) — The epsilon parameter in Adam, which is a small constant for numerical stability.amsgrad (
bool, optional, default toFalse) — Whether to apply AMSGrad variant of this algorithm or not, see On the Convergence of Adam and Beyond.weight_decay_rate (
float, optional, defaults to 0) — The weight decay to apply.include_in_weight_decay (
List[str], optional) — List of the parameter names (or re patterns) to apply weight decay to. If none is passed, weight decay is applied to all parameters by default (unless they are inexclude_from_weight_decay).exclude_from_weight_decay (
List[str], optional) — List of the parameter names (or re patterns) to exclude from applying weight decay to. If ainclude_in_weight_decayis passed, the names in it will supersede this list.name (
str, optional, defaults to ‘AdamWeightDecay’) — Optional name for the operations created when applying gradients.kwargs (
Dict[str, Any], optional) — Keyword arguments. Allowed to be {clipnorm,clipvalue,lr,decay}.clipnormis clip gradients by norm;clipvalueis clip gradients by value,decayis included for backward compatibility to allow time inverse decay of learning rate.lris included for backward compatibility, recommended to uselearning_rateinstead.
Adam enables L2 weight decay and clip_by_global_norm on gradients. Just adding the square of the weights to the loss function is not the correct way of using L2 regularization/weight decay with Adam, since that will interact with the m and v parameters in strange ways as shown in Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization.
Instead we want to decay the weights in a manner that doesn’t interact with the m/v parameters. This is equivalent to adding the square of the weights to the loss with plain (non-momentum) SGD.
from_config
( config )
Creates an optimizer from its config with WarmUp custom object.
transformers.create_optimizer
( init_lr: floatnum_train_steps: intnum_warmup_steps: intmin_lr_ratio: float = 0.0adam_beta1: float = 0.9adam_beta2: float = 0.999adam_epsilon: float = 1e-08adam_clipnorm: typing.Optional[float] = Noneadam_global_clipnorm: typing.Optional[float] = Noneweight_decay_rate: float = 0.0power: float = 1.0include_in_weight_decay: typing.Optional[typing.List[str]] = None )
Parameters
init_lr (
float) — The desired learning rate at the end of the warmup phase.num_train_steps (
int) — The total number of training steps.num_warmup_steps (
int) — The number of warmup steps.min_lr_ratio (
float, optional, defaults to 0) — The final learning rate at the end of the linear decay will beinit_lr * min_lr_ratio.adam_beta1 (
float, optional, defaults to 0.9) — The beta1 to use in Adam.adam_beta2 (
float, optional, defaults to 0.999) — The beta2 to use in Adam.adam_epsilon (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-8) — The epsilon to use in Adam.adam_clipnorm (
float, optional, defaults toNone) — If notNone, clip the gradient norm for each weight tensor to this value.adam_global_clipnorm (
float, optional, defaults toNone) — If notNone, clip gradient norm to this value. When using this argument, the norm is computed over all weight tensors, as if they were concatenated into a single vector.weight_decay_rate (
float, optional, defaults to 0) — The weight decay to use.power (
float, optional, defaults to 1.0) — The power to use for PolynomialDecay.include_in_weight_decay (
List[str], optional) — List of the parameter names (or re patterns) to apply weight decay to. If none is passed, weight decay is applied to all parameters except bias and layer norm parameters.
Creates an optimizer with a learning rate schedule using a warmup phase followed by a linear decay.
Schedules
Learning Rate Schedules (Pytorch)
class transformers.SchedulerType
( valuenames = Nonemodule = Nonequalname = Nonetype = Nonestart = 1 )
An enumeration.
transformers.get_scheduler
( name: typing.Union[str, transformers.trainer_utils.SchedulerType]optimizer: Optimizernum_warmup_steps: typing.Optional[int] = Nonenum_training_steps: typing.Optional[int] = None )
Parameters
name (
strorSchedulerType) — The name of the scheduler to use.optimizer (
torch.optim.Optimizer) — The optimizer that will be used during training.num_warmup_steps (
int, optional) — The number of warmup steps to do. This is not required by all schedulers (hence the argument being optional), the function will raise an error if it’s unset and the scheduler type requires it.num_training_steps (`int“, optional) — The number of training steps to do. This is not required by all schedulers (hence the argument being optional), the function will raise an error if it’s unset and the scheduler type requires it.
Unified API to get any scheduler from its name.
transformers.get_constant_schedule
( optimizer: Optimizerlast_epoch: int = -1 )
Parameters
optimizer (
~torch.optim.Optimizer) — The optimizer for which to schedule the learning rate.last_epoch (
int, optional, defaults to -1) — The index of the last epoch when resuming training.
Create a schedule with a constant learning rate, using the learning rate set in optimizer.
transformers.get_constant_schedule_with_warmup
( optimizer: Optimizernum_warmup_steps: intlast_epoch: int = -1 )
Parameters
optimizer (
~torch.optim.Optimizer) — The optimizer for which to schedule the learning rate.num_warmup_steps (
int) — The number of steps for the warmup phase.last_epoch (
int, optional, defaults to -1) — The index of the last epoch when resuming training.
Create a schedule with a constant learning rate preceded by a warmup period during which the learning rate increases linearly between 0 and the initial lr set in the optimizer.
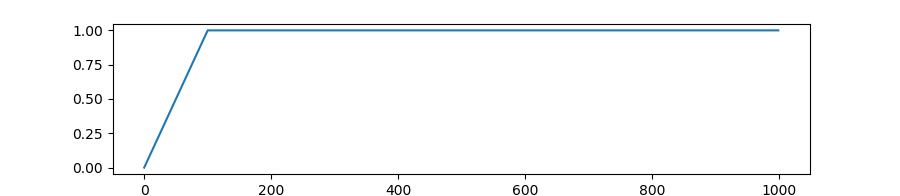
transformers.get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup
( optimizer: Optimizernum_warmup_steps: intnum_training_steps: intnum_cycles: float = 0.5last_epoch: int = -1 )
Parameters
optimizer (
~torch.optim.Optimizer) — The optimizer for which to schedule the learning rate.num_warmup_steps (
int) — The number of steps for the warmup phase.num_training_steps (
int) — The total number of training steps.num_cycles (
float, optional, defaults to 0.5) — The number of waves in the cosine schedule (the defaults is to just decrease from the max value to 0 following a half-cosine).last_epoch (
int, optional, defaults to -1) — The index of the last epoch when resuming training.
Create a schedule with a learning rate that decreases following the values of the cosine function between the initial lr set in the optimizer to 0, after a warmup period during which it increases linearly between 0 and the initial lr set in the optimizer.
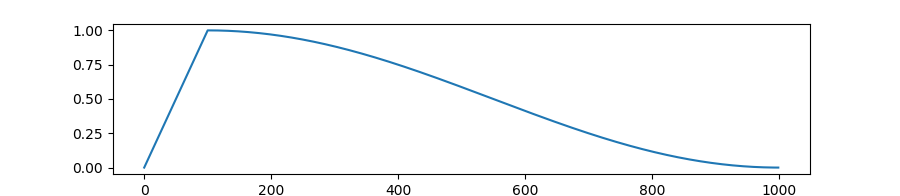
transformers.get_cosine_with_hard_restarts_schedule_with_warmup
( optimizer: Optimizernum_warmup_steps: intnum_training_steps: intnum_cycles: int = 1last_epoch: int = -1 )
Parameters
optimizer (
~torch.optim.Optimizer) — The optimizer for which to schedule the learning rate.num_warmup_steps (
int) — The number of steps for the warmup phase.num_training_steps (
int) — The total number of training steps.num_cycles (
int, optional, defaults to 1) — The number of hard restarts to use.last_epoch (
int, optional, defaults to -1) — The index of the last epoch when resuming training.
Create a schedule with a learning rate that decreases following the values of the cosine function between the initial lr set in the optimizer to 0, with several hard restarts, after a warmup period during which it increases linearly between 0 and the initial lr set in the optimizer.
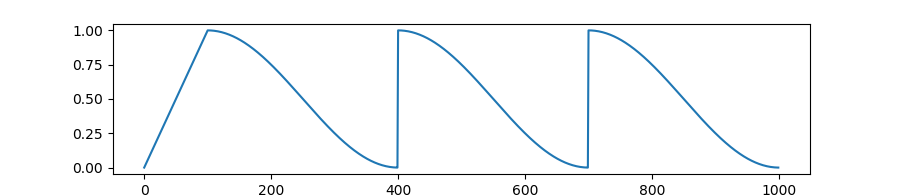
transformers.get_linear_schedule_with_warmup
( optimizernum_warmup_stepsnum_training_stepslast_epoch = -1 )
Parameters
optimizer (
~torch.optim.Optimizer) — The optimizer for which to schedule the learning rate.num_warmup_steps (
int) — The number of steps for the warmup phase.num_training_steps (
int) — The total number of training steps.last_epoch (
int, optional, defaults to -1) — The index of the last epoch when resuming training.
Create a schedule with a learning rate that decreases linearly from the initial lr set in the optimizer to 0, after a warmup period during which it increases linearly from 0 to the initial lr set in the optimizer.
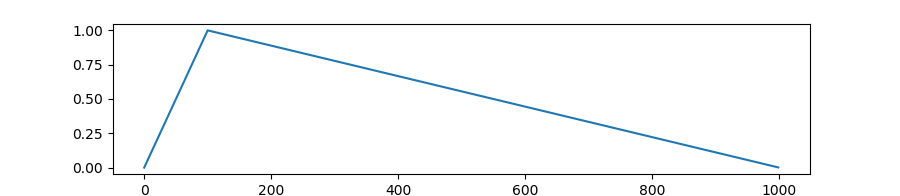
transformers.get_polynomial_decay_schedule_with_warmup
( optimizernum_warmup_stepsnum_training_stepslr_end = 1e-07power = 1.0last_epoch = -1 )
Parameters
optimizer (
~torch.optim.Optimizer) — The optimizer for which to schedule the learning rate.num_warmup_steps (
int) — The number of steps for the warmup phase.num_training_steps (
int) — The total number of training steps.lr_end (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-7) — The end LR.power (
float, optional, defaults to 1.0) — Power factor.last_epoch (
int, optional, defaults to -1) — The index of the last epoch when resuming training.
Create a schedule with a learning rate that decreases as a polynomial decay from the initial lr set in the optimizer to end lr defined by lr_end, after a warmup period during which it increases linearly from 0 to the initial lr set in the optimizer.
Note: power defaults to 1.0 as in the fairseq implementation, which in turn is based on the original BERT implementation at https://github.com/google-research/bert/blob/f39e881b169b9d53bea03d2d341b31707a6c052b/optimization.py#L37
transformers.get_inverse_sqrt_schedule
( optimizer: Optimizernum_warmup_steps: inttimescale: int = Nonelast_epoch: int = -1 )
Parameters
optimizer (
~torch.optim.Optimizer) — The optimizer for which to schedule the learning rate.num_warmup_steps (
int) — The number of steps for the warmup phase.timescale (
int, optional, defaults tonum_warmup_steps) — Time scale.last_epoch (
int, optional, defaults to -1) — The index of the last epoch when resuming training.
Create a schedule with an inverse square-root learning rate, from the initial lr set in the optimizer, after a warmup period which increases lr linearly from 0 to the initial lr set in the optimizer.
Warmup (TensorFlow)
class transformers.WarmUp
( initial_learning_rate: floatdecay_schedule_fn: typing.Callablewarmup_steps: intpower: float = 1.0name: str = None )
Parameters
initial_learning_rate (
float) — The initial learning rate for the schedule after the warmup (so this will be the learning rate at the end of the warmup).decay_schedule_fn (
Callable) — The schedule function to apply after the warmup for the rest of training.warmup_steps (
int) — The number of steps for the warmup part of training.power (
float, optional, defaults to 1) — The power to use for the polynomial warmup (defaults is a linear warmup).name (
str, optional) — Optional name prefix for the returned tensors during the schedule.
Applies a warmup schedule on a given learning rate decay schedule.
Gradient Strategies
GradientAccumulator (TensorFlow)
class transformers.GradientAccumulator
( )
Gradient accumulation utility. When used with a distribution strategy, the accumulator should be called in a replica context. Gradients will be accumulated locally on each replica and without synchronization. Users should then call .gradients, scale the gradients if required, and pass the result to apply_gradients.
reset
( )
Resets the accumulated gradients on the current replica.
Last updated