ResNet
ResNet
Overview
The ResNet model was proposed in Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition by Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren and Jian Sun. Our implementation follows the small changes made by Nvidia, we apply the stride=2 for downsampling in bottleneck’s 3x3 conv and not in the first 1x1. This is generally known as “ResNet v1.5”.
ResNet introduced residual connections, they allow to train networks with an unseen number of layers (up to 1000). ResNet won the 2015 ILSVRC & COCO competition, one important milestone in deep computer vision.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
Deeper neural networks are more difficult to train. We present a residual learning framework to ease the training of networks that are substantially deeper than those used previously. We explicitly reformulate the layers as learning residual functions with reference to the layer inputs, instead of learning unreferenced functions. We provide comprehensive empirical evidence showing that these residual networks are easier to optimize, and can gain accuracy from considerably increased depth. On the ImageNet dataset we evaluate residual nets with a depth of up to 152 layers---8x deeper than VGG nets but still having lower complexity. An ensemble of these residual nets achieves 3.57% error on the ImageNet test set. This result won the 1st place on the ILSVRC 2015 classification task. We also present analysis on CIFAR-10 with 100 and 1000 layers. The depth of representations is of central importance for many visual recognition tasks. Solely due to our extremely deep representations, we obtain a 28% relative improvement on the COCO object detection dataset. Deep residual nets are foundations of our submissions to ILSVRC & COCO 2015 competitions, where we also won the 1st places on the tasks of ImageNet detection, ImageNet localization, COCO detection, and COCO segmentation.
Tips:
One can use AutoImageProcessor to prepare images for the model.
The figure below illustrates the architecture of ResNet. Taken from the original paper.
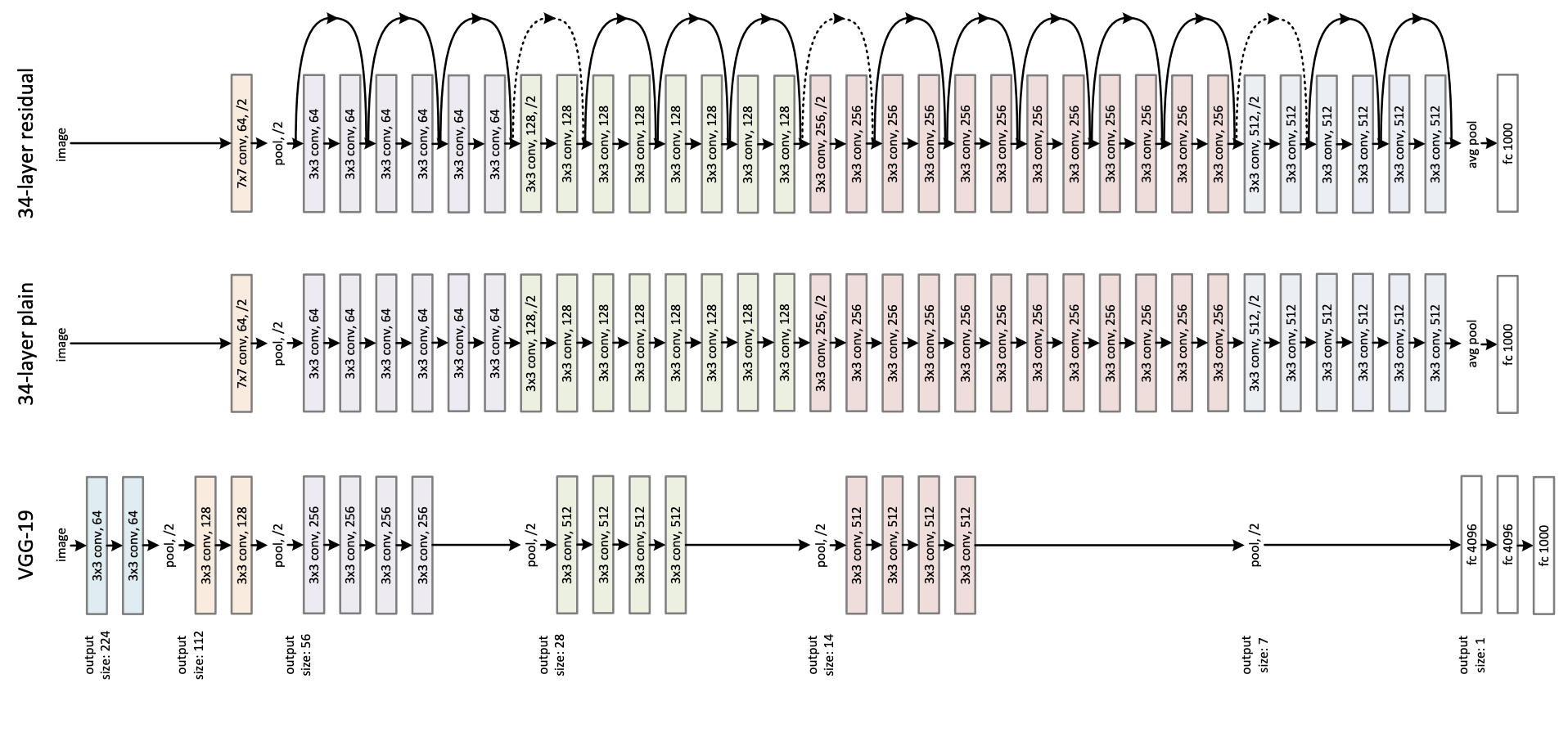
This model was contributed by Francesco. The TensorFlow version of this model was added by amyeroberts. The original code can be found here.
Resources
A list of official BOINC AI and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with ResNet.
Image Classification
ResNetForImageClassification is supported by this example script and notebook.
See also: Image classification task guide
If you’re interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we’ll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
ResNetConfig
class transformers.ResNetConfig
( num_channels = 3embedding_size = 64hidden_sizes = [256, 512, 1024, 2048]depths = [3, 4, 6, 3]layer_type = 'bottleneck'hidden_act = 'relu'downsample_in_first_stage = Falseout_features = Noneout_indices = None**kwargs )
Parameters
num_channels (
int, optional, defaults to 3) — The number of input channels.embedding_size (
int, optional, defaults to 64) — Dimensionality (hidden size) for the embedding layer.hidden_sizes (
List[int], optional, defaults to[256, 512, 1024, 2048]) — Dimensionality (hidden size) at each stage.depths (
List[int], optional, defaults to[3, 4, 6, 3]) — Depth (number of layers) for each stage.layer_type (
str, optional, defaults to"bottleneck") — The layer to use, it can be either"basic"(used for smaller models, like resnet-18 or resnet-34) or"bottleneck"(used for larger models like resnet-50 and above).hidden_act (
str, optional, defaults to"relu") — The non-linear activation function in each block. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new"are supported.downsample_in_first_stage (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — IfTrue, the first stage will downsample the inputs using astrideof 2.out_features (
List[str], optional) — If used as backbone, list of features to output. Can be any of"stem","stage1","stage2", etc. (depending on how many stages the model has). If unset andout_indicesis set, will default to the corresponding stages. If unset andout_indicesis unset, will default to the last stage.out_indices (
List[int], optional) — If used as backbone, list of indices of features to output. Can be any of 0, 1, 2, etc. (depending on how many stages the model has). If unset andout_featuresis set, will default to the corresponding stages. If unset andout_featuresis unset, will default to the last stage.
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a ResNetModel. It is used to instantiate an ResNet model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the ResNet microsoft/resnet-50 architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
Copied
ResNetModel
class transformers.ResNetModel
( config )
Parameters
config (ResNetConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The bare ResNet model outputting raw features without any specific head on top. This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( pixel_values: Tensoroutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPoolingAndNoAttention or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See ConvNextImageProcessor.call() for details.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPoolingAndNoAttention or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPoolingAndNoAttention or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (ResNetConfig) and inputs.
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model.pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Last layer hidden-state after a pooling operation on the spatial dimensions.hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
The ResNetModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
Copied
ResNetForImageClassification
class transformers.ResNetForImageClassification
( config )
Parameters
config (ResNetConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
ResNet Model with an image classification head on top (a linear layer on top of the pooled features), e.g. for ImageNet.
This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = Nonelabels: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See ConvNextImageProcessor.call() for details.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — Labels for computing the image classification/regression loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels > 1a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (ResNetConfig) and inputs.
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) loss.logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) scores (before SoftMax).hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the model at the output of each stage.
The ResNetForImageClassification forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
Copied
TFResNetModel
class transformers.TFResNetModel
( *args**kwargs )
Parameters
config (ResNetConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The bare ResNet model outputting raw features without any specific head on top. This model is a TensorFlow tf.keras.layers.Layer sub-class. Use it as a regular TensorFlow Module and refer to the TensorFlow documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
call
( pixel_values: Tensoroutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonetraining: bool = False ) → transformers.modeling_tf_outputs.TFBaseModelOutputWithPoolingAndNoAttention or tuple(tf.Tensor)
Parameters
pixel_values (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See ConvNextImageProcessor.call() for details.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.modeling_tf_outputs.TFBaseModelOutputWithPoolingAndNoAttention or tuple(tf.Tensor)
A transformers.modeling_tf_outputs.TFBaseModelOutputWithPoolingAndNoAttention or a tuple of tf.Tensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (ResNetConfig) and inputs.
last_hidden_state (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model.pooler_output (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Last layer hidden-state after a pooling operation on the spatial dimensions.hidden_states (
tuple(tf.Tensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftf.Tensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
The TFResNetModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
Copied
TFResNetForImageClassification
class transformers.TFResNetForImageClassification
( *args**kwargs )
Parameters
config (ResNetConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
ResNet Model with an image classification head on top (a linear layer on top of the pooled features), e.g. for ImageNet.
This model is a TensorFlow tf.keras.layers.Layer sub-class. Use it as a regular TensorFlow Module and refer to the TensorFlow documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
call
( pixel_values: Tensor = Nonelabels: Tensor = Noneoutput_hidden_states: bool = Nonereturn_dict: bool = Nonetraining: bool = False ) → transformers.modeling_tf_outputs.TFImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention or tuple(tf.Tensor)
Parameters
pixel_values (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See ConvNextImageProcessor.call() for details.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.labels (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — Labels for computing the image classification/regression loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels > 1a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
Returns
transformers.modeling_tf_outputs.TFImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention or tuple(tf.Tensor)
A transformers.modeling_tf_outputs.TFImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention or a tuple of tf.Tensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (ResNetConfig) and inputs.
loss (
tf.Tensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) loss.logits (
tf.Tensorof shape(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) scores (before SoftMax).hidden_states (
tuple(tf.Tensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftf.Tensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the model at the output of each stage.
The TFResNetForImageClassification forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
Copied
FlaxResNetModel
class transformers.FlaxResNetModel
( config: ResNetConfiginput_shape = (1, 224, 224, 3)seed: int = 0dtype: dtype = <class 'jax.numpy.float32'>_do_init: bool = True**kwargs )
Parameters
config (ResNetConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
dtype (
jax.numpy.dtype, optional, defaults tojax.numpy.float32) — The data type of the computation. Can be one ofjax.numpy.float32,jax.numpy.float16(on GPUs) andjax.numpy.bfloat16(on TPUs).This can be used to enable mixed-precision training or half-precision inference on GPUs or TPUs. If specified all the computation will be performed with the given
dtype.Note that this only specifies the dtype of the computation and does not influence the dtype of model parameters.
If you wish to change the dtype of the model parameters, see to_fp16() and to_bf16().
The bare ResNet model outputting raw features without any specific head on top.
This model inherits from FlaxPreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading, saving and converting weights from PyTorch models)
This model is also a Flax Linen flax.linen.Module subclass. Use it as a regular Flax linen Module and refer to the Flax documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
Finally, this model supports inherent JAX features such as:
__call__
( pixel_valuesparams: dict = Nonetrain: bool = Falseoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxBaseModelOutputWithPoolingAndNoAttention or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Returns
transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxBaseModelOutputWithPoolingAndNoAttention or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxBaseModelOutputWithPoolingAndNoAttention or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.resnet.configuration_resnet.ResNetConfig'>) and inputs.
last_hidden_state (
jnp.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model.pooler_output (
jnp.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Last layer hidden-state after a pooling operation on the spatial dimensions.hidden_states (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width). Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
The FlaxResNetPreTrainedModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Copied
FlaxResNetForImageClassification
class transformers.FlaxResNetForImageClassification
( config: ResNetConfiginput_shape = (1, 224, 224, 3)seed: int = 0dtype: dtype = <class 'jax.numpy.float32'>_do_init: bool = True**kwargs )
Parameters
config (ResNetConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
dtype (
jax.numpy.dtype, optional, defaults tojax.numpy.float32) — The data type of the computation. Can be one ofjax.numpy.float32,jax.numpy.float16(on GPUs) andjax.numpy.bfloat16(on TPUs).This can be used to enable mixed-precision training or half-precision inference on GPUs or TPUs. If specified all the computation will be performed with the given
dtype.Note that this only specifies the dtype of the computation and does not influence the dtype of model parameters.
If you wish to change the dtype of the model parameters, see to_fp16() and to_bf16().
ResNet Model with an image classification head on top (a linear layer on top of the pooled features), e.g. for ImageNet.
This model inherits from FlaxPreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading, saving and converting weights from PyTorch models)
This model is also a Flax Linen flax.linen.Module subclass. Use it as a regular Flax linen Module and refer to the Flax documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
Finally, this model supports inherent JAX features such as:
__call__
( pixel_valuesparams: dict = Nonetrain: bool = Falseoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Returns
transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.resnet.configuration_resnet.ResNetConfig'>) and inputs.
logits (
jnp.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) scores (before SoftMax).hidden_states (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True): Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the model at the output of each stage.
The FlaxResNetPreTrainedModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
Copied
Last updated