Deformable DETR
Deformable DETR
Overview
The Deformable DETR model was proposed in Deformable DETR: Deformable Transformers for End-to-End Object Detection by Xizhou Zhu, Weijie Su, Lewei Lu, Bin Li, Xiaogang Wang, Jifeng Dai. Deformable DETR mitigates the slow convergence issues and limited feature spatial resolution of the original DETR by leveraging a new deformable attention module which only attends to a small set of key sampling points around a reference.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
DETR has been recently proposed to eliminate the need for many hand-designed components in object detection while demonstrating good performance. However, it suffers from slow convergence and limited feature spatial resolution, due to the limitation of Transformer attention modules in processing image feature maps. To mitigate these issues, we proposed Deformable DETR, whose attention modules only attend to a small set of key sampling points around a reference. Deformable DETR can achieve better performance than DETR (especially on small objects) with 10 times less training epochs. Extensive experiments on the COCO benchmark demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
Tips:
One can use DeformableDetrImageProcessor to prepare images (and optional targets) for the model.
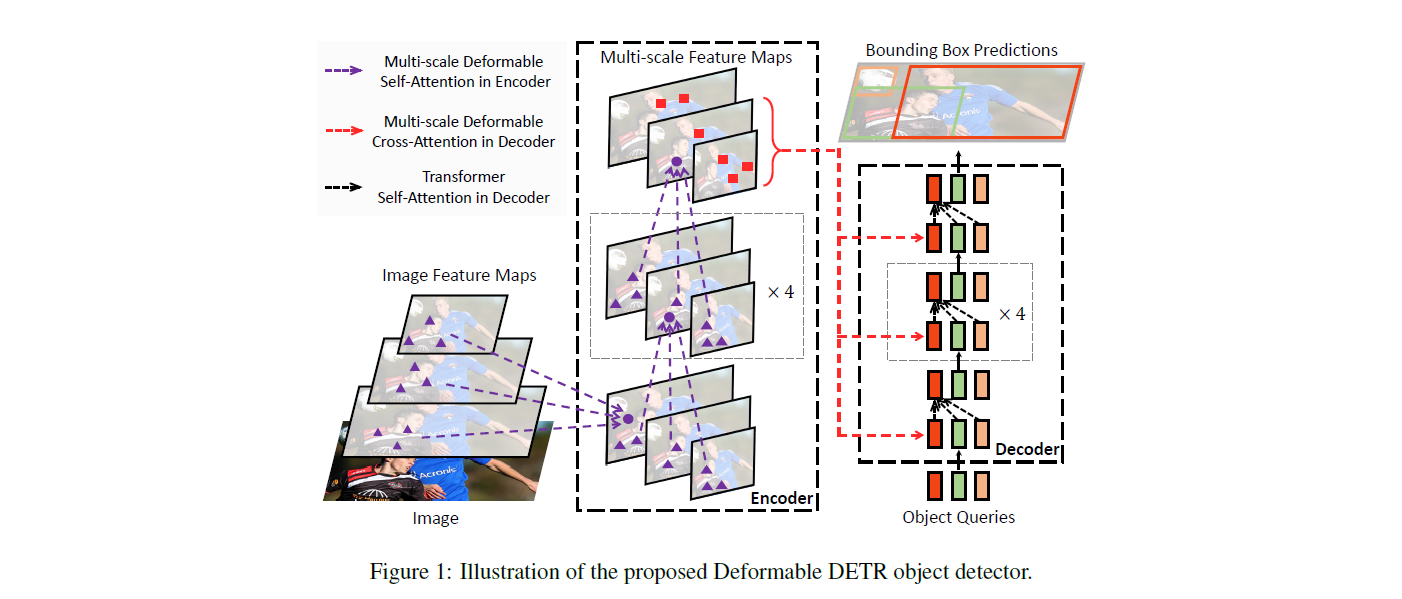
Deformable DETR architecture. Taken from the original paper.
This model was contributed by nielsr. The original code can be found here.
Resources
A list of official BOINC AI and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with Deformable DETR.
Object Detection
Demo notebooks regarding inference + fine-tuning on a custom dataset for DeformableDetrForObjectDetection can be found here.
See also: Object detection task guide.
If you’re interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we’ll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
DeformableDetrImageProcessor
class transformers.DeformableDetrImageProcessor
( format: typing.Union[str, transformers.models.deformable_detr.image_processing_deformable_detr.AnnotionFormat] = <AnnotionFormat.COCO_DETECTION: 'coco_detection'>do_resize: bool = Truesize: typing.Dict[str, int] = Noneresample: Resampling = <Resampling.BILINEAR: 2>do_rescale: bool = Truerescale_factor: typing.Union[int, float] = 0.00392156862745098do_normalize: bool = Trueimage_mean: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float]] = Noneimage_std: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float]] = Nonedo_pad: bool = True**kwargs )
Parameters
format (
str, optional, defaults to"coco_detection") — Data format of the annotations. One of “coco_detection” or “coco_panoptic”.do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Controls whether to resize the image’s (height, width) dimensions to the specifiedsize. Can be overridden by thedo_resizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod.size (
Dict[str, int]optional, defaults to{"shortest_edge" -- 800, "longest_edge": 1333}): Size of the image’s (height, width) dimensions after resizing. Can be overridden by thesizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod.resample (
PILImageResampling, optional, defaults toPILImageResampling.BILINEAR) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image.do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Controls whether to rescale the image by the specified scalerescale_factor. Can be overridden by thedo_rescaleparameter in thepreprocessmethod.rescale_factor (
intorfloat, optional, defaults to1/255) — Scale factor to use if rescaling the image. Can be overridden by therescale_factorparameter in thepreprocessmethod. do_normalize — Controls whether to normalize the image. Can be overridden by thedo_normalizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod.image_mean (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_DEFAULT_MEAN) — Mean values to use when normalizing the image. Can be a single value or a list of values, one for each channel. Can be overridden by theimage_meanparameter in thepreprocessmethod.image_std (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_DEFAULT_STD) — Standard deviation values to use when normalizing the image. Can be a single value or a list of values, one for each channel. Can be overridden by theimage_stdparameter in thepreprocessmethod.do_pad (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Controls whether to pad the image to the largest image in a batch and create a pixel mask. Can be overridden by thedo_padparameter in thepreprocessmethod.
Constructs a Deformable DETR image processor.
preprocess
( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), typing.List[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image')], typing.List[numpy.ndarray], typing.List[ForwardRef('torch.Tensor')]]annotations: typing.Union[typing.Dict[str, typing.Union[int, str, typing.List[typing.Dict]]], typing.List[typing.Dict[str, typing.Union[int, str, typing.List[typing.Dict]]]], NoneType] = Nonereturn_segmentation_masks: bool = Nonemasks_path: typing.Union[str, pathlib.Path, NoneType] = Nonedo_resize: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonesize: typing.Union[typing.Dict[str, int], NoneType] = Noneresample = Nonedo_rescale: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonerescale_factor: typing.Union[int, float, NoneType] = Nonedo_normalize: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneimage_mean: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = Noneimage_std: typing.Union[float, typing.List[float], NoneType] = Nonedo_pad: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneformat: typing.Union[str, transformers.models.deformable_detr.image_processing_deformable_detr.AnnotionFormat, NoneType] = Nonereturn_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = Nonedata_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension] = <ChannelDimension.FIRST: 'channels_first'>input_data_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension, NoneType] = None**kwargs )
Parameters
images (
ImageInput) — Image or batch of images to preprocess. Expects a single or batch of images with pixel values ranging from 0 to 255. If passing in images with pixel values between 0 and 1, setdo_rescale=False.annotations (
AnnotationTypeorList[AnnotationType], optional) — List of annotations associated with the image or batch of images. If annotation is for object detection, the annotations should be a dictionary with the following keys:“image_id” (
int): The image id.“annotations” (
List[Dict]): List of annotations for an image. Each annotation should be a dictionary. An image can have no annotations, in which case the list should be empty. If annotation is for segmentation, the annotations should be a dictionary with the following keys:“image_id” (
int): The image id.“segments_info” (
List[Dict]): List of segments for an image. Each segment should be a dictionary. An image can have no segments, in which case the list should be empty.“file_name” (
str): The file name of the image.
return_segmentation_masks (
bool, optional, defaults to self.return_segmentation_masks) — Whether to return segmentation masks.masks_path (
strorpathlib.Path, optional) — Path to the directory containing the segmentation masks.do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults to self.do_resize) — Whether to resize the image.size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults to self.size) — Size of the image after resizing.resample (
PILImageResampling, optional, defaults to self.resample) — Resampling filter to use when resizing the image.do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults to self.do_rescale) — Whether to rescale the image.rescale_factor (
float, optional, defaults to self.rescale_factor) — Rescale factor to use when rescaling the image.do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults to self.do_normalize) — Whether to normalize the image.image_mean (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults to self.image_mean) — Mean to use when normalizing the image.image_std (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults to self.image_std) — Standard deviation to use when normalizing the image.do_pad (
bool, optional, defaults to self.do_pad) — Whether to pad the image.format (
strorAnnotionFormat, optional, defaults to self.format) — Format of the annotations.return_tensors (
strorTensorType, optional, defaults to self.return_tensors) — Type of tensors to return. IfNone, will return the list of images.data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional, defaults toChannelDimension.FIRST) — The channel dimension format for the output image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format.Unset: Use the channel dimension format of the input image.
input_data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional) — The channel dimension format for the input image. If unset, the channel dimension format is inferred from the input image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format."none"orChannelDimension.NONE: image in (height, width) format.
Preprocess an image or a batch of images so that it can be used by the model.
post_process_object_detection
( outputsthreshold: float = 0.5target_sizes: typing.Union[transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, typing.List[typing.Tuple]] = Nonetop_k: int = 100 ) → List[Dict]
Parameters
outputs (
DetrObjectDetectionOutput) — Raw outputs of the model.threshold (
float, optional) — Score threshold to keep object detection predictions.target_sizes (
torch.TensororList[Tuple[int, int]], optional) — Tensor of shape(batch_size, 2)or list of tuples (Tuple[int, int]) containing the target size (height, width) of each image in the batch. If left to None, predictions will not be resized.top_k (
int, optional, defaults to 100) — Keep only top k bounding boxes before filtering by thresholding.
Returns
List[Dict]
A list of dictionaries, each dictionary containing the scores, labels and boxes for an image in the batch as predicted by the model.
Converts the raw output of DeformableDetrForObjectDetection into final bounding boxes in (top_left_x, top_left_y, bottom_right_x, bottom_right_y) format. Only supports PyTorch.
DeformableDetrFeatureExtractor
class transformers.DeformableDetrFeatureExtractor
( *args**kwargs )
__call__
( images**kwargs )
Preprocess an image or a batch of images.
post_process_object_detection
( outputsthreshold: float = 0.5target_sizes: typing.Union[transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, typing.List[typing.Tuple]] = Nonetop_k: int = 100 ) → List[Dict]
Parameters
outputs (
DetrObjectDetectionOutput) — Raw outputs of the model.threshold (
float, optional) — Score threshold to keep object detection predictions.target_sizes (
torch.TensororList[Tuple[int, int]], optional) — Tensor of shape(batch_size, 2)or list of tuples (Tuple[int, int]) containing the target size (height, width) of each image in the batch. If left to None, predictions will not be resized.top_k (
int, optional, defaults to 100) — Keep only top k bounding boxes before filtering by thresholding.
Returns
List[Dict]
A list of dictionaries, each dictionary containing the scores, labels and boxes for an image in the batch as predicted by the model.
Converts the raw output of DeformableDetrForObjectDetection into final bounding boxes in (top_left_x, top_left_y, bottom_right_x, bottom_right_y) format. Only supports PyTorch.
DeformableDetrConfig
class transformers.DeformableDetrConfig
( use_timm_backbone = Truebackbone_config = Nonenum_channels = 3num_queries = 300max_position_embeddings = 1024encoder_layers = 6encoder_ffn_dim = 1024encoder_attention_heads = 8decoder_layers = 6decoder_ffn_dim = 1024decoder_attention_heads = 8encoder_layerdrop = 0.0is_encoder_decoder = Trueactivation_function = 'relu'd_model = 256dropout = 0.1attention_dropout = 0.0activation_dropout = 0.0init_std = 0.02init_xavier_std = 1.0return_intermediate = Trueauxiliary_loss = Falseposition_embedding_type = 'sine'backbone = 'resnet50'use_pretrained_backbone = Truedilation = Falsenum_feature_levels = 4encoder_n_points = 4decoder_n_points = 4two_stage = Falsetwo_stage_num_proposals = 300with_box_refine = Falseclass_cost = 1bbox_cost = 5giou_cost = 2mask_loss_coefficient = 1dice_loss_coefficient = 1bbox_loss_coefficient = 5giou_loss_coefficient = 2eos_coefficient = 0.1focal_alpha = 0.25disable_custom_kernels = False**kwargs )
Parameters
use_timm_backbone (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether or not to use thetimmlibrary for the backbone. If set toFalse, will use theAutoBackboneAPI.backbone_config (
PretrainedConfigordict, optional) — The configuration of the backbone model. Only used in caseuse_timm_backboneis set toFalsein which case it will default toResNetConfig().num_channels (
int, optional, defaults to 3) — The number of input channels.num_queries (
int, optional, defaults to 300) — Number of object queries, i.e. detection slots. This is the maximal number of objects DeformableDetrModel can detect in a single image. In casetwo_stageis set toTrue, we usetwo_stage_num_proposalsinstead.d_model (
int, optional, defaults to 256) — Dimension of the layers.encoder_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 6) — Number of encoder layers.decoder_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 6) — Number of decoder layers.encoder_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 8) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the Transformer encoder.decoder_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 8) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the Transformer decoder.decoder_ffn_dim (
int, optional, defaults to 1024) — Dimension of the “intermediate” (often named feed-forward) layer in decoder.encoder_ffn_dim (
int, optional, defaults to 1024) — Dimension of the “intermediate” (often named feed-forward) layer in decoder.activation_function (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"relu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. If string,"gelu","relu","silu"and"gelu_new"are supported.dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — The dropout probability for all fully connected layers in the embeddings, encoder, and pooler.attention_dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout ratio for the attention probabilities.activation_dropout (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout ratio for activations inside the fully connected layer.init_std (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices.init_xavier_std (
float, optional, defaults to 1) — The scaling factor used for the Xavier initialization gain in the HM Attention map module.encoder_layerdrop (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The LayerDrop probability for the encoder. See the [LayerDrop paper](see https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.11556) for more details.auxiliary_loss (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether auxiliary decoding losses (loss at each decoder layer) are to be used.position_embedding_type (
str, optional, defaults to"sine") — Type of position embeddings to be used on top of the image features. One of"sine"or"learned".backbone (
str, optional, defaults to"resnet50") — Name of convolutional backbone to use in caseuse_timm_backbone=True. Supports any convolutional backbone from the timm package. For a list of all available models, see this page.use_pretrained_backbone (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to use pretrained weights for the backbone. Only supported whenuse_timm_backbone=True.dilation (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to replace stride with dilation in the last convolutional block (DC5). Only supported whenuse_timm_backbone=True.class_cost (
float, optional, defaults to 1) — Relative weight of the classification error in the Hungarian matching cost.bbox_cost (
float, optional, defaults to 5) — Relative weight of the L1 error of the bounding box coordinates in the Hungarian matching cost.giou_cost (
float, optional, defaults to 2) — Relative weight of the generalized IoU loss of the bounding box in the Hungarian matching cost.mask_loss_coefficient (
float, optional, defaults to 1) — Relative weight of the Focal loss in the panoptic segmentation loss.dice_loss_coefficient (
float, optional, defaults to 1) — Relative weight of the DICE/F-1 loss in the panoptic segmentation loss.bbox_loss_coefficient (
float, optional, defaults to 5) — Relative weight of the L1 bounding box loss in the object detection loss.giou_loss_coefficient (
float, optional, defaults to 2) — Relative weight of the generalized IoU loss in the object detection loss.eos_coefficient (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — Relative classification weight of the ‘no-object’ class in the object detection loss.num_feature_levels (
int, optional, defaults to 4) — The number of input feature levels.encoder_n_points (
int, optional, defaults to 4) — The number of sampled keys in each feature level for each attention head in the encoder.decoder_n_points (
int, optional, defaults to 4) — The number of sampled keys in each feature level for each attention head in the decoder.two_stage (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to apply a two-stage deformable DETR, where the region proposals are also generated by a variant of Deformable DETR, which are further fed into the decoder for iterative bounding box refinement.two_stage_num_proposals (
int, optional, defaults to 300) — The number of region proposals to be generated, in casetwo_stageis set toTrue.with_box_refine (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to apply iterative bounding box refinement, where each decoder layer refines the bounding boxes based on the predictions from the previous layer.focal_alpha (
float, optional, defaults to 0.25) — Alpha parameter in the focal loss.disable_custom_kernels (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Disable the use of custom CUDA and CPU kernels. This option is necessary for the ONNX export, as custom kernels are not supported by PyTorch ONNX export.
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a DeformableDetrModel. It is used to instantiate a Deformable DETR model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the Deformable DETR SenseTime/deformable-detr architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Examples:
Copied
DeformableDetrModel
class transformers.DeformableDetrModel
( config: DeformableDetrConfig )
Parameters
config (DeformableDetrConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The bare Deformable DETR Model (consisting of a backbone and encoder-decoder Transformer) outputting raw hidden-states without any specific head on top.
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( pixel_values: FloatTensorpixel_mask: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = Nonedecoder_attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = Noneencoder_outputs: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = Noneinputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = Nonedecoder_inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = Noneoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.deformable_detr.modeling_deformable_detr.DeformableDetrModelOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See DeformableDetrImageProcessor.call() for details.
pixel_mask (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, height, width), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding pixel values. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:1 for pixels that are real (i.e. not masked),
0 for pixels that are padding (i.e. masked).
decoder_attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_queries), optional) — Not used by default. Can be used to mask object queries.encoder_outputs (
tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional) — Tuple consists of (last_hidden_state, optional:hidden_states, optional:attentions)last_hidden_stateof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) is a sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the encoder. Used in the cross-attention of the decoder.inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Optionally, instead of passing the flattened feature map (output of the backbone + projection layer), you can choose to directly pass a flattened representation of an image.decoder_inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_queries, hidden_size), optional) — Optionally, instead of initializing the queries with a tensor of zeros, you can choose to directly pass an embedded representation.output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.
Returns
transformers.models.deformable_detr.modeling_deformable_detr.DeformableDetrModelOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.deformable_detr.modeling_deformable_detr.DeformableDetrModelOutput or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (DeformableDetrConfig) and inputs.
init_reference_points (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_queries, 4)) — Initial reference points sent through the Transformer decoder.last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_queries, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the decoder of the model.intermediate_hidden_states (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, config.decoder_layers, num_queries, hidden_size)) — Stacked intermediate hidden states (output of each layer of the decoder).intermediate_reference_points (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, config.decoder_layers, num_queries, 4)) — Stacked intermediate reference points (reference points of each layer of the decoder).decoder_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_queries, hidden_size). Hidden-states of the decoder at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.decoder_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, num_queries, num_queries). Attentions weights of the decoder, after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_queries, num_heads, 4, 4). Attentions weights of the decoder’s cross-attention layer, after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the cross-attention heads.encoder_last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the encoder of the model.encoder_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states of the encoder at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.encoder_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_queries, num_heads, 4, 4). Attentions weights of the encoder, after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.enc_outputs_class (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, config.num_labels), optional, returned whenconfig.with_box_refine=Trueandconfig.two_stage=True) — Predicted bounding boxes scores where the topconfig.two_stage_num_proposalsscoring bounding boxes are picked as region proposals in the first stage. Output of bounding box binary classification (i.e. foreground and background).enc_outputs_coord_logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, 4), optional, returned whenconfig.with_box_refine=Trueandconfig.two_stage=True) — Logits of predicted bounding boxes coordinates in the first stage.
The DeformableDetrModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Copied
DeformableDetrForObjectDetection
class transformers.DeformableDetrForObjectDetection
( config: DeformableDetrConfig )
Parameters
config (DeformableDetrConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
Deformable DETR Model (consisting of a backbone and encoder-decoder Transformer) with object detection heads on top, for tasks such as COCO detection.
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
( pixel_values: FloatTensorpixel_mask: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = Nonedecoder_attention_mask: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = Noneencoder_outputs: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = Noneinputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = Nonedecoder_inputs_embeds: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = Nonelabels: typing.Optional[typing.List[dict]] = Noneoutput_attentions: typing.Optional[bool] = Noneoutput_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = Nonereturn_dict: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.models.deformable_detr.modeling_deformable_detr.DeformableDetrObjectDetectionOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it.Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See DeformableDetrImageProcessor.call() for details.
pixel_mask (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, height, width), optional) — Mask to avoid performing attention on padding pixel values. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:1 for pixels that are real (i.e. not masked),
0 for pixels that are padding (i.e. masked).
decoder_attention_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_queries), optional) — Not used by default. Can be used to mask object queries.encoder_outputs (
tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional) — Tuple consists of (last_hidden_state, optional:hidden_states, optional:attentions)last_hidden_stateof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) is a sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the encoder. Used in the cross-attention of the decoder.inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Optionally, instead of passing the flattened feature map (output of the backbone + projection layer), you can choose to directly pass a flattened representation of an image.decoder_inputs_embeds (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_queries, hidden_size), optional) — Optionally, instead of initializing the queries with a tensor of zeros, you can choose to directly pass an embedded representation.output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail.output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple.labels (
List[Dict]of len(batch_size,), optional) — Labels for computing the bipartite matching loss. List of dicts, each dictionary containing at least the following 2 keys: ‘class_labels’ and ‘boxes’ (the class labels and bounding boxes of an image in the batch respectively). The class labels themselves should be atorch.LongTensorof len(number of bounding boxes in the image,)and the boxes atorch.FloatTensorof shape(number of bounding boxes in the image, 4).
Returns
transformers.models.deformable_detr.modeling_deformable_detr.DeformableDetrObjectDetectionOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.deformable_detr.modeling_deformable_detr.DeformableDetrObjectDetectionOutput or a tuple of torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various elements depending on the configuration (DeformableDetrConfig) and inputs.
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsare provided)) — Total loss as a linear combination of a negative log-likehood (cross-entropy) for class prediction and a bounding box loss. The latter is defined as a linear combination of the L1 loss and the generalized scale-invariant IoU loss.loss_dict (
Dict, optional) — A dictionary containing the individual losses. Useful for logging.logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_queries, num_classes + 1)) — Classification logits (including no-object) for all queries.pred_boxes (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_queries, 4)) — Normalized boxes coordinates for all queries, represented as (center_x, center_y, width, height). These values are normalized in [0, 1], relative to the size of each individual image in the batch (disregarding possible padding). You can use~DeformableDetrProcessor.post_process_object_detectionto retrieve the unnormalized bounding boxes.auxiliary_outputs (
list[Dict], optional) — Optional, only returned when auxilary losses are activated (i.e.config.auxiliary_lossis set toTrue) and labels are provided. It is a list of dictionaries containing the two above keys (logitsandpred_boxes) for each decoder layer.last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_queries, hidden_size), optional) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the decoder of the model.decoder_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_queries, hidden_size). Hidden-states of the decoder at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.decoder_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, num_queries, num_queries). Attentions weights of the decoder, after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.cross_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_queries, num_heads, 4, 4). Attentions weights of the decoder’s cross-attention layer, after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the cross-attention heads.encoder_last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size), optional) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the encoder of the model.encoder_hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states of the encoder at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.encoder_attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, num_heads, 4, 4). Attentions weights of the encoder, after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.intermediate_hidden_states (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, config.decoder_layers, num_queries, hidden_size)) — Stacked intermediate hidden states (output of each layer of the decoder).intermediate_reference_points (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, config.decoder_layers, num_queries, 4)) — Stacked intermediate reference points (reference points of each layer of the decoder).init_reference_points (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_queries, 4)) — Initial reference points sent through the Transformer decoder.enc_outputs_class (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, config.num_labels), optional, returned whenconfig.with_box_refine=Trueandconfig.two_stage=True) — Predicted bounding boxes scores where the topconfig.two_stage_num_proposalsscoring bounding boxes are picked as region proposals in the first stage. Output of bounding box binary classification (i.e. foreground and background).enc_outputs_coord_logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, 4), optional, returned whenconfig.with_box_refine=Trueandconfig.two_stage=True) — Logits of predicted bounding boxes coordinates in the first stage.
The DeformableDetrForObjectDetection forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
Copied
Last updated