InstructPix2Pix Training
InstructPix2Pix
InstructPix2Pix is a method to fine-tune text-conditioned diffusion models such that they can follow an edit instruction for an input image. Models fine-tuned using this method take the following as inputs:
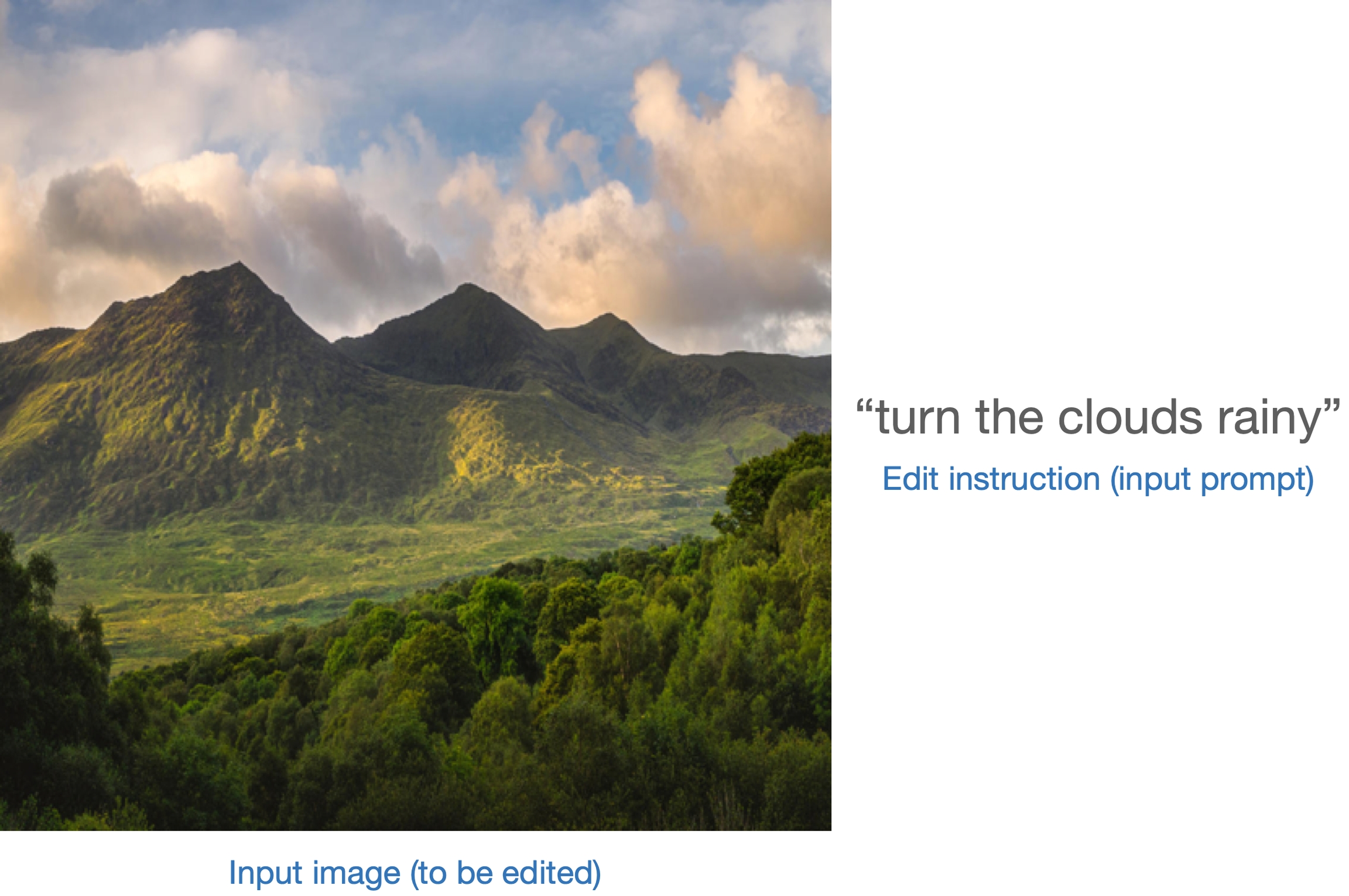
The output is an “edited” image that reflects the edit instruction applied on the input image:
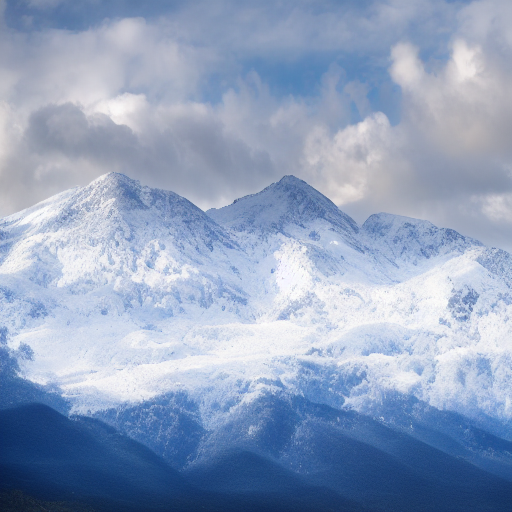

The train_instruct_pix2pix.py script (you can find the it here) shows how to implement the training procedure and adapt it for Stable Diffusion.
Disclaimer: Even though train_instruct_pix2pix.py implements the InstructPix2Pix training procedure while being faithful to the original implementation we have only tested it on a small-scale dataset. This can impact the end results. For better results, we recommend longer training runs with a larger dataset. Here you can find a large dataset for InstructPix2Pix training.
Running locally with PyTorch
Installing the dependencies
Before running the scripts, make sure to install the library’s training dependencies:
Important
To make sure you can successfully run the latest versions of the example scripts, we highly recommend installing from source and keeping the install up to date as we update the example scripts frequently and install some example-specific requirements. To do this, execute the following steps in a new virtual environment:
Copied
Then cd in the example folder
Copied
Now run
Copied
And initialize an 🌍 Accelerate environment with:
Copied
Or for a default accelerate configuration without answering questions about your environment
Copied
Or if your environment doesn’t support an interactive shell e.g. a notebook
Copied
Toy example
As mentioned before, we’ll use a small toy dataset for training. The dataset is a smaller version of the original dataset used in the InstructPix2Pix paper. To use your own dataset, take a look at the Create a dataset for training guide.
Specify the MODEL_NAME environment variable (either a Hub model repository id or a path to the directory containing the model weights) and pass it to the pretrained_model_name_or_path argument. You’ll also need to specify the dataset name in DATASET_ID:
Copied
Now, we can launch training. The script saves all the components (feature_extractor, scheduler, text_encoder, unet, etc) in a subfolder in your repository.
Copied
Additionally, we support performing validation inference to monitor training progress with Weights and Biases. You can enable this feature with report_to="wandb":
Copied
We recommend this type of validation as it can be useful for model debugging. Note that you need wandb installed to use this. You can install wandb by running pip install wandb.
Here, you can find an example training run that includes some validation samples and the training hyperparameters.
Note: In the original paper, the authors observed that even when the model is trained with an image resolution of 256x256, it generalizes well to bigger resolutions such as 512x512. This is likely because of the larger dataset they used during training.
Training with multiple GPUs
accelerate allows for seamless multi-GPU training. Follow the instructions here for running distributed training with accelerate. Here is an example command:
Copied
Inference
Once training is complete, we can perform inference:
Copied
An example model repo obtained using this training script can be found here - sayakpaul/instruct-pix2pix.
We encourage you to play with the following three parameters to control speed and quality during performance:
num_inference_stepsimage_guidance_scaleguidance_scale
Particularly, image_guidance_scale and guidance_scale can have a profound impact on the generated (“edited”) image (see here for an example).
If you’re looking for some interesting ways to use the InstructPix2Pix training methodology, we welcome you to check out this blog post: Instruction-tuning Stable Diffusion with InstructPix2Pix.
Stable Diffusion XL
Training with Stable Diffusion XL is also supported via the train_instruct_pix2pix_sdxl.py script. Please refer to the docs here.
Last updated