User Access Tokens
User access tokens
What are User Access Tokens?
User Access Tokens are the preferred way to authenticate an application or notebook to Hugging Face services. You can manage your access tokens in your settings.
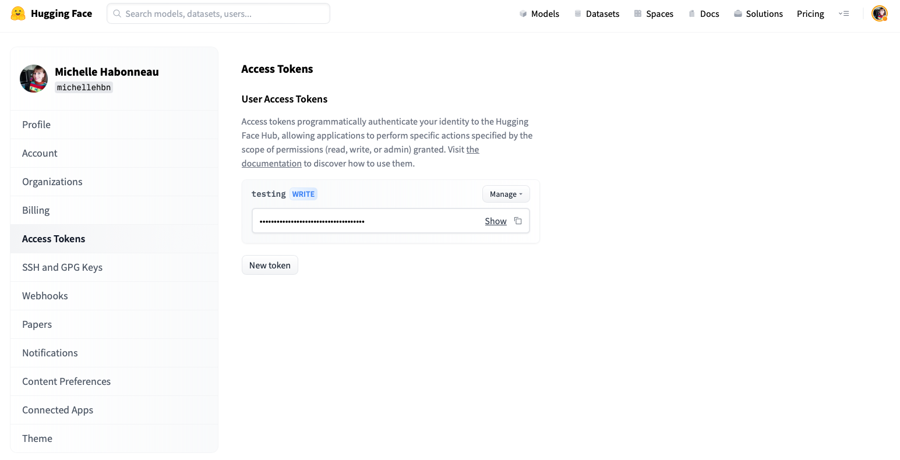
Access tokens allow applications and notebooks to perform specific actions specified by the scope of the roles shown in the following:
read: tokens with this role can only be used to provide read access to repositories you could read. That includes public and private repositories that you, or an organization you’re a member of, own. Use this role if you only need to read content from the Hugging Face Hub (e.g. when downloading private models or doing inference).write: tokens with this role additionally grant write access to the repositories you have write access to. Use this token if you need to create or push content to a repository (e.g., when training a model or modifying a model card).
Note that Organization API Tokens have been deprecated:
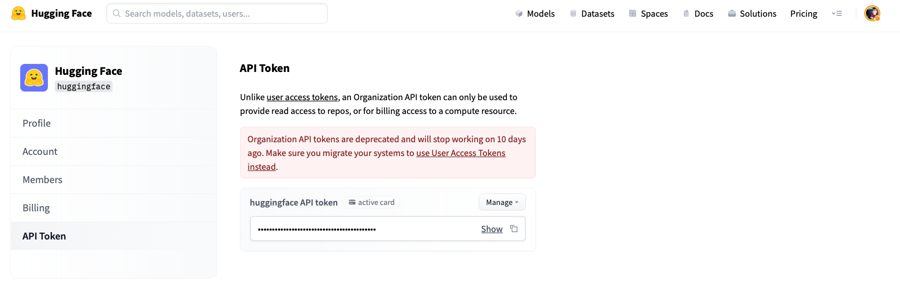
If you are a member of an organization with read/write/admin role, then your User Access Tokens will be able to read/write the resources according to the token permission (read/write) and organization membership (read/write/admin).
How to manage User Access Tokens?
To create an access token, go to your settings, then click on the Access Tokens tab. Click on the New token button to create a new User Access Token.
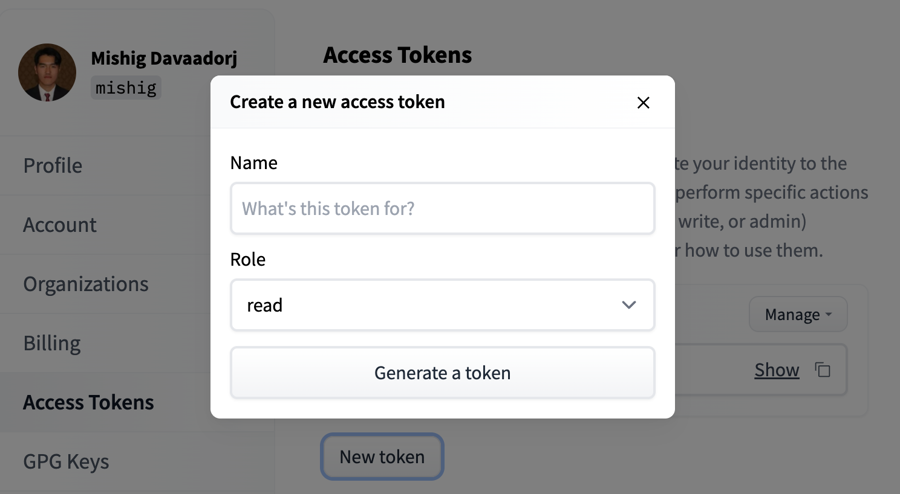
Select a role and a name for your token and voilà - you’re ready to go!
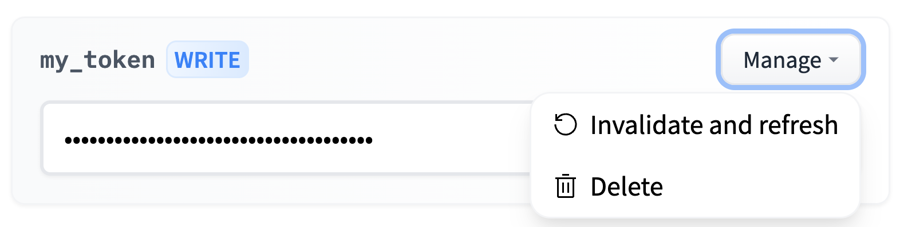
You can delete and refresh User Access Tokens by clicking on the Manage button.
How to use User Access Tokens?
There are plenty of ways to use a User Access Token to access the Hugging Face Hub, granting you the flexibility you need to build awesome apps on top of it.
User Access Tokens can be:
used in place of a password to access the Hugging Face Hub with git or with basic authentication.
passed as a bearer token when calling the Inference API.
used in the Hugging Face Python libraries, such as
transformersordatasets:
Copied
Try not to leak your token! Though you can always rotate it, anyone will be able to read or write your private repos in the meantime which is 💩
Best practices
We recommend you create one access token per app or usage. For instance, you could have a separate token for:
A local machine.
A Colab notebook.
An awesome custom inference server.
This way, you can invalidate one token without impacting your other usages.
We also recommend only giving the appropriate role to each token you create. If you only need read access (e.g., loading a dataset with the datasets library or retrieving the weights of a model), only give your access token the read role.
Last updated